 |
 |
| J Navig Port Res > Volume 44(4); 2020 > Article |
|
ņÜö ņĢĮ
ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņŚÉņä£ ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ĻĖ░ņŚģļōżņØĆ ļ╣äĒĢ®ļ”¼ņĀüņØĖ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØä ņäĀĒāØĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓ĮņÜ░Ļ░Ć ņ׳ņ£╝ļ®░, ņØ┤ļ¤¼ĒĢ£ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļŖö ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ĻĖ░ņŚģļōżņŚÉ ļ¦ēļīĆĒĢ£ ņåÉņŗżņØä ņ£Āļ░£ņŗ£Ēé©ļŗż. ņØ┤ļ¤¼ĒĢ£ ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢ ņäĀĒāØņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļČäņäØņØä ļ│Ė ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļŖö Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖ ņØ┤ļĪĀ ņżæ ņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦ü ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņÖĆ ļ¦żļ¬░ ļ╣äņÜ® ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ ņØ┤ļĪĀņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĀæĻĘ╝ ĒĢśņśĆņ£╝ļ®░, ņäżļ¼Ėņ¦Ćļ▓ĢĻ│╝ ņé¼ļĪĆ ļČäņäØ ļ░®ļ▓ĢļĪĀņ£╝ļĪ£ ļģ╝ļ¼ĖņØä ņ×æņä▒ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ļČäņäØ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝, Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖ ņØ┤ļĪĀņØĖ ņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦ü ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņÖĆ ļ¦żļ¬░ ļ╣äņÜ® ĒÜ©Ļ│╝Ļ░Ć ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņŚÉ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣£ļŗżļŖö ņé¼ņŗżĻ│╝ ņØ┤ļ¤¼ĒĢ£ ņśüĒ¢źņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņ×ÉĻ░Ć ļ╣äĒĢ®ļ”¼ņĀüņØĖ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØä ņäĀĒāØĒĢśĻ▓ī ļÉĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗżļŖö ņé¼ņŗżņØä ļ░£Ļ▓¼Ē¢łļŗż.
ABSTRACT
Shipping companies have suffered additional losses because of irrational shipping finance decisions. This paper analyses the cases according to the behavioral finance theories. The theories of behavioral finance used in the analysis and research of this paper are the anchoring effect and sunk cost effect. The backgrounds and reasons for the decisions regarding ship financing are analysed based on the questionnaire responses and case studies. As a result of the analysis, it is found that the behavioral finance theories, anchoring effect, and sunk cost effect, have effects on the ship financing decisions, that errors related to behavioral finance can result in irrational decisions, and that shipping companies suffered additional losses because of the behavioral finance errors.
ņĀĆļ¬ģĒĢ£ Ē¢ēļÅÖĻ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖņ×É ļŗżļŗłņŚś ņ╣┤ļäłļ©╝ņØ┤ 2002ļģäņŚÉ ļģĖļ▓©Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖņāüņØä ņłśņŚ¼ ļ░øņØĆļŹ░ ņØ┤ņ¢┤, ņŗ£ņ╣┤Ļ│Ā ļīĆĒĢÖĻĄÉņØś Ē¢ēļÅÖĻ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖņ×É ļ”¼ņ░©ļō£ ņäĖņØ╝ļ¤¼ ĻĄÉņłśĻ░Ć 2017ļģäņŚÉ ļśÉļŗżņŗ£ ļģĖļ▓©Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖņāüņØä ļ░øņ£╝ļ®░, Ē¢ēļÅÖĻ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖ Ļ│╝ Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖņØĆ ļ╣äņŻ╝ļźś ĒĢÖļ¼ĖņŚÉņä£ ņżæņÜöĒĢ£ ĒĢÖļ¼Ėņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ▒░ļōŁļéśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż. ņĀäĒåĄņĀü Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖ Ļ┤ĆņĀÉņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņØĖĻ░äņØä ĒĢ®ļ”¼ņĀü ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņ×ÉļĪ£ ĒīÉļŗ©ĒĢśĻĖ░ņŚÉ Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ņŚÉņä£ ļ╣äĒÜ©ņ£©ņä▒ņØ┤ ļ░£ņāØĒĢśļ®┤ ĻĘĖ ņøÉņØĖņØä ņŗ£ņןĻ│╝ ņĀĢļČĆņØś ĻĖ░ļŖź ļ¼ĖņĀ£ Ēś╣ņØĆ ņĀ£ļÅä ļō▒ņØś ļ¼ĖņĀ£ļĪ£ ņāØĻ░üĒĢśĻ│Ā, ņØ┤ļź╝ ĻĄÉņĀĢĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ņä£ ņŗ£ņןņØ┤ļōĀ ĻĄŁĻ░ĆļōĀ ĻĘĖ ņĀ£ļÅäņĀü ņĖĪļ®┤ņŚÉ ņŻ╝ņØśļź╝ ĻĖ░ņÜĖņŚ¼ņĢ╝ ĒĢ£ļŗżĻ│Ā ņŻ╝ņןĒĢ£ļŗż(Baddeley, 2017, Wilkinson and Klaes, 2012; Camerer et al., 2004).
ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī, Ē¢ēļÅÖĻ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖņ×ÉļōżņØĆ ņØĖĻ░äņØĆ ĒĢ®ļ”¼ņĀü Ē¢ēņ£äņ×ÉĻ░Ć ņĢäļŗłļØ╝ļŖö Ļ┤ĆņĀÉņØä ņ¦ĆņåŹņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņŻ╝ņןĒĢśņśĆļŗż. Ē¢ēļÅÖĻ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖņ×ÉļōżņØĆ Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ņŚÉņä£ ņ¢┤ļ¢ż ļ╣äĒÜ©ņ£©ņä▒ņØ┤ ļ│┤ņØ┤ļ®┤, ĻĘĖ ņøÉņØĖņØä ņŗ£ņןņØś ņŗżĒī©ļéś ņĀ£ļÅäņØś ņŗżĒī©Ļ░Ć ņĢäļŗłļØ╝, Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ņŻ╝ņ▓┤ļōż ņ”ē, ņé¼ļ×īļōżņØś ļ╣äĒĢ®ļ”¼ņä▒ņŚÉņä£ ĻĘĖ ņøÉņØĖņØä ņ░ŠņĢśļŗż (Baddeley, 2017; Chen et al., 2017, Barberis and Thaler, 2002).
ņśłļź╝ ļōżņ¢┤, ņĀäĒåĄ Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖņŚÉņä£ļŖö ļ¼╝Ļ▒┤ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ Ļ░Ćņ╣śĻ░Ć Ļ░ĆĻ▓®ņØä ņāüĒÜīĒĢśļ®┤ ņåīļ╣äņ×É ņ×ēņŚ¼Ļ░Ć ļ░£ņāØĒĢśļ»ĆļĪ£ ļ¼╝Ļ▒┤ ĻĄ¼ņ×ģņØä ĒĢśĻ▓ī ļÉśņ¦Ćļ¦ī, Ē¢ēļÅÖĻ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņåīļ╣äņ×É ņ×ēņŚ¼Ļ░Ć ļ░£ņāØĒĢśļŹöļØ╝ļÅä, ĻĘĖ Ļ░ĆĻ▓®ņØ┤ ņś©ļØ╝ņØĖ ĒīÉļ¦ż Ļ░ĆĻ▓®ļ│┤ļŗż ļåÆņ£╝ļ®┤ ĻĄ¼ņ×ģņØä ĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖļŖö ĒśäņāüņØ┤ ļ░£ņāØĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ļŗż. ņןĻĖ░ ĻĖ░ņ”ØņŚÉņä£ļÅä ņé¼ļ×īļōżņØĆ ņØ╝ļ░śņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņןĻĖ░ ĻĖ░ņ”ØņŚÉ ĻĖŹņĀĢņĀüņØ┤ņ¦Ćļ¦ī, ļ»ĖĻĄŁĻ│╝ ņ£Āļ¤ĮņØś ņןĻĖ░ ĻĖ░ņ”Ø ļÅÖņØś ļ╣äņ£©ņØĆ ņ░©ņØ┤Ļ░Ć ļé£ļŗż. ņןĻĖ░ ĻĖ░ņ”Ø Ļ▒░ļČĆ ņØśņé¼ Ēæ£ņŗ£ļĪ£ ņןĻĖ░ ĻĖ░ņ”Ø ļÅÖņØś ņŚ¼ļČĆļź╝ ņäĀĒāØĒĢśļŖö ņ£Āļ¤ĮĻĄŁĻ░Ć ņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņןĻĖ░ ĻĖ░ņ”Ø ļÅÖņØś ļ╣äņ£©ņØ┤ 90% ņØ┤ņāüņØĖ ļŹ░ ļ╣äĒĢ┤ ņןĻĖ░ ĻĖ░ņ”Ø ņ░ĖņŚ¼ ņØśņé¼ Ēæ£ņŗ£ļĪ£ ņןĻĖ░ ĻĖ░ņ”Ø ļÅÖņØś ņŚ¼ļČĆļź╝ ņäĀĒāØĒĢśļŖö ļ»ĖĻĄŁņØĆ ņןĻĖ░ ĻĖ░ņ”Ø ļÅÖņØś ļ╣äņ£©ņØ┤ 20% ļ»Ėļ¦īņØä ĻĖ░ļĪØĒĢśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż. ņŗ£ņןĻ│╝ ņĀĢļČĆņØś ĻĖ░ļŖźĻ│╝ ņĀ£ļÅä ļ│┤ļŗżļŖö ņØĖĻ░ä ņŗ¼ļ”¼ļéś Ē¢ēĒā£Ļ░Ć Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ ļŗżļź┤Ļ▓ī ļ¦īļōżņ¢┤ļāäņØä ņāüĻĖ░ ņśłļź╝ ĒåĄĒĢśņŚ¼ ņĢī ņłś ņ׳ļŗż(Baddeley, 2017).
ĒĢ£ĒÄĖ 2008ļģä ļ”¼ļ¦ī ņé¼Ēā£ņÖĆ 2017ļģä ĒĢ£ņ¦äĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ Ēīīņé░ ļō▒ņØś ņśüĒ¢źņ£╝ļĪ£ ĻĄŁļé┤ ĻĖłņ£ĄĻĖ░Ļ┤ĆļōżņØĆņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£ĄņŚÉņä£ņŚäņ▓Łļé£ņåÉņŗżņØäņ×ģņŚłņ£╝ļ®░, ļ»╝Ļ░äņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņŗ£ņןņØĆĻĘĖĻĖ░ļŖźņØäņÖäņĀäĒ׳ņāüņŗżĒĢśĻ▓īļÉśņŚłļŗż. ĒŖ╣Ē׳, ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņŗ£ņןĒśĖĒÖ®ĻĖ░ļź╝ Ļ▒░ņ│É ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ ņŗ£ĒÖ®ņØ┤ ĻĖēļØĮĒĢśļŖö ņŗ£ĻĖ░ņŚÉ ĻĖ░ ļ░£ņŻ╝ĒĢ£ ņäĀļ░ĢļōżņØś ņØĖļÅäļź╝ ĒżĻĖ░ĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖĻ│Ā, ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£ĄņØä ņŗżĒ¢ēĒĢśņŚ¼ ņäĀļ░ĢļōżņØä ņØĖļÅäļ░øņØĆ ĻĄŁļé┤ ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņé¼ļōżņØĆ ļåÆņØĆ ņäĀĻ░ĆņÖĆ ņøÉĻ░Ć ļĢīļ¼ĖņŚÉ Ļ▓Įņśüņāü ņ¢┤ļĀżņøĆņØä Ļ▓¬Ļ▒░ļéś Ēīīņé░ĒĢśņśĆļŗż(Kim and Park, 2016; Seok 2020). ĻĘĖ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝, ĻĄŁļé┤ ĻĖłņ£ĄĻĖ░Ļ┤ĆļōżņØĆ ļ¦ēļīĆĒĢ£ ņåÉņŗżņØä ņ×ģĻ│Ā ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņŗ£ņןņŚÉņä£ ņ▓ĀņłśĒĢśņśĆņ£╝ļ®░, Ēśäņ×¼ļŖö ĻĄŁņ▒ģ ĻĖłņ£ĄĻĖ░Ļ┤ĆļōżņØś ņ¦ĆņøÉņŚÉ ņØśņ¦ĆĒĢśļ®░ ĻĄŁļé┤ ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņé¼ļōżņØ┤ ņ¢┤ļĀĄĻ▓ī ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£ĄņØä ĒÖĢļ│┤ĒĢśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż (Jeon et al., 2017).
ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ĻĖ░ņŚģļōżņØ┤Ļ▓Įņśüņāüņ¢┤ļĀżņøĆņØäĻ▓¬Ļ▒░ļéśĒīīņé░ņØäĒĢśĻ│Ā, ĻĖłņ£ĄĻĖ░Ļ┤ĆļōżņØ┤ ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ąņ£╝ļĪ£ņØĖĒĢśņŚ¼ļ¦ēļīĆĒĢ£ņåÉņŗżņØäņ×ģņØĆņøÉņØĖņżæņŚÉļŖöĒ¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖņ×ÉļōżņØ┤ ņŻ╝ņןĒĢśļŖö ļ░öņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØ┤ ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ĻĖ░ņŚģ Ļ▓Įņśüņ×ÉņÖĆ ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ļŗ┤ļŗ╣ņ×ÉļōżņØś ļ╣äĒĢ®ļ”¼ņĀü ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØ┤ ņ¦üņĀæņĀüņØĖ ņøÉņØĖņØ┤ ļÉśņŚłļŗżĻ│Ā ņČöņĀĢĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż. ĒŖ╣Ē׳, ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņŗ£ĒÖ®ĒĢśļØĮņŗ£, ĻĖ░ļ░£ņŻ╝ĒĢ£ņäĀļ░ĢņŚÉļīĆĒĢ┤ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņé¼ļōżņØ┤ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£ĄņØä ņĪ░ļŗ¼ĒĢśļŖö Ļ│╝ņĀĢņŚÉņä£ Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖ ņØ┤ļĪĀņŚÉ ļ¬ģņŗ£ļÉ£ ļ¦żļ¬░ļ╣äņÜ®ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņÖĆ ņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦ü ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņØś ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ░øņĢä ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņŗ£ ļ╣äĒĢ®ļ”¼ņĀüņØĖ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØä ļé┤ļ”¼ņ¦ĆļŖö ņĢŖņĢśļŖöņ¦Ć ņØśņŗ¼ņØ┤ ļÉ£ļŗż.
ņØ┤ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą Ļ┤ĆļĀ© ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØä ņ¦äĒ¢ēĒĢĀ ļĢī ņØĖĻ░äņØś ņŗ¼ļ”¼ņĀü ņÜöņØĖļōżņØ┤ ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņŚÉ ņ¢┤ļ¢╗Ļ▓ī ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣śļŖöņ¦Ćļź╝ ņäżļ¼ĖņĪ░ņé¼ņÖĆ ņé¼ļĪĆ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ ļ░®ļ▓ĢņØä ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ļČäņäØĒĢśļĀżĻ│Ā ĒĢ£ļŗż. ļśÉĒĢ£, ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņŚÉņä£ļ░£ņāØĒĢ£ņśżļźśļōżņØ┤ņ¢┤ļ¢ĀĒĢ£Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ļ░£ņāØņŗ£ņ╝░ļŖöņ¦ĆļČäņäØĒĢśĻ│Āņ×É ĒĢ£ļŗż. ņØ┤ļź╝ ĒåĄĒĢśņŚ¼ ņäĀļ░Ģ ĻĖłņ£ĄņŚÉņä£ ļéśĒāĆļéśļŖö ļ╣äĒĢ®ļ”¼ņĀü ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØä Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖņØś ņŗ£Ļ░üņŚÉņä£ ļģ╝ņØśĒĢśĻ│Ā, ĻĄŁļé┤ ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņé¼ņÖĆ ĻĖłņ£ĄĻĖ░Ļ┤ĆņØś ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ļŗ┤ļŗ╣ņ×ÉļōżņØ┤ ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņŗżĒ¢ēņŗ£ ļ▓öĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ļ╣äĒĢ®ļ”¼ņĀüņØĖ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØä ņżäņØ┤ļŖöļŹ░ ļÅäņøĆņØä ņŻ╝Ļ│Āņ×É ĒĢ£ļŗż.
Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖņØĆ ļŗżļźĖ ņé¼ĒÜīĻ│╝ĒĢÖņ▓śļ¤╝ ņé¼ļ×īļōżņØ┤ ņé┤ņĢäĻ░ĆļŖö ņäĖņāüņØä ļ│┤ļŗż ļŹö ņל ņØ┤ĒĢ┤ĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ ņØ┤ļĪĀļōżņØä Ļ░£ļ░£ņŗ£ņ╝£ ļéśĻ░ĆļŖö ĒĢÖļ¼ĖņØ┤ļŗż. Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖ ņØ┤ļĪĀļōżņØĆ Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ ĒśäņāüļōżņØä ņĀĢĒÖĢĒĢśĻ▓ī ļ¼śņé¼ĒĢśĻ│Ā ņäżļ¬ģĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ ļģĖļĀźĒĢ£ļŗż. ņŗĀĻ│ĀņĀäņŻ╝ņØś Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖņØĆ 19ņäĖĻĖ░ļČĆĒä░ ļ░£ņĀäļÉśņ¢┤ ņÖöņ£╝ļ®░, ĒÜ©ņÜ®ņØś ĻĘ╣ļīĆĒÖö, ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØś ĒĢ®ļ”¼ņä▒, ņłśņÜöņÖĆ Ļ│ĄĻĖē ļō▒ņØä ļ░öĒāĢņ£╝ ļĪ£ Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ ĒÖ£ļÅÖņØä ņל ņäżļ¬ģĒĢśļŖö ņØ┤ļĪĀļōżņØä Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖņ×ÉļōżņØ┤ ņĀ£Ļ│ĄĒĢśĻ│Ā ņ׳ ņ£╝ļ®░ ļ¦żņÜ░ ņ£ĀņÜ®ĒĢ£ ĒĢÖļ¼Ėņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØĖņŗØļÉśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż. ļśÉĒĢ£, ņŗĀĻ│ĀņĀäņŻ╝ņØś Ļ▓Į ņĀ£ĒĢÖņØĆ Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖ ļ░£ņĀäņŚÉ ļ¦ÄņØĆ Ļ│ĄĒŚīņØä ĒĢ┤ņśżĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż. ĻĘĖļ¤¼ļéś ņĀäĒåĄņĀüņØĖ Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖ ņØ┤ļĪĀļōżņØĆ ņØ╝ļČĆ Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ ĒśäņāüļōżņØä ļ¬ģĒÖĢĒĢśĻ▓ī ņäżļ¬ģĒĢśĻ▒░ļéś ļ¼ś ņé¼ĒĢśņ¦Ć ļ¬╗Ē¢łļŗż. ņśłļź╝ ļōżņ¢┤ ņåÉņŗżĒÜīĒö╝ņĀü ņä▒Ē¢źņØ┤ļéś ļ»ĖļלņØś Ēü░ ņØ┤ ņØĄļ│┤ļŗż Ēśäņ×¼ņØś ņ×æņØĆ ņØ┤ņØĄņŚÉ ļŹö ņ¦æņżæĒĢśļŖö Ēśäņāü ļō▒ ņĀäĒåĄņĀü Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ ĒĢÖ ņØ┤ļĪĀņ£╝ļĪ£ ņäżļ¬ģĒĢśĻĖ░Ļ░Ć ņ¢┤ļĀżņøĀļŗż (Wilkinson and Klaes, 2012; Camerer et al., 2004). ĒŖ╣Ē׳, 1980ļģäļīĆ ņØ┤ņĀäņŚÉļŖö Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖ ņ×ÉļōżņØ┤ ņŗ¼ļ”¼ĒĢÖņØä ļ¼┤ņŗ£Ē¢łĻ│Ā, Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖ Ļ│ĄļČĆņŚÉ ņŗ¼ļ”¼ĒĢÖņØä ņĀæļ¬®ņŗ£ĒéżļŖö ņŗ£ļÅäļŖö ĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņĢśļŗż(Baddeley, 2017).
ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī, 1980ļģäļīĆļČĆĒä░ ņŗ¼ļ”¼ĒĢÖ ĻĖ░ļ░śņØĖ Ē¢ēļÅÖĻ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖņØ┤ ĒĢÖĻ│äņŚÉņä£ ņØĖņĀĢļ░øĻĖ░ ņŗ£ņ×æĒ¢łļŗż. Ē¢ēļÅÖĻ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖņØĆ ņĀäĒåĄņĀü Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖņØ┤ ņäżļ¬ģĒĢśņ¦Ć ļ¬╗ĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ ĒśäņāüļōżņØä ļ¬ģņŠīĒĢśĻ▓ī ņäżļ¬ģĒĢśņśĆļŗż(Baddeley, 2017; Wilkinson and Klaes, 2012; Camerer et al., 2004).
Ļ░ĆļĀ╣, ĻĖłņ£Ąņŗ£ņן, ņŻ╝ņŗØņŗ£ņןĻ│╝ ņŻ╝ņŗØ ļ¦żļ¦ż Ē¢ēĒā£ļōżņØĆ ņĀäĒåĄņĀü Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖ Ēī©ļ¤¼ļŗżņ×äņ£╝ļĪ£ņäżļ¬ģĒĢśĻĖ░ņ¢┤ļĀżņøĀļŗż. ņÖ£ļāÉĒĢśļ®┤, Ēł¼ņ×Éļź╝ņ¦æĒ¢ēĒĢ£ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņ×ÉļōżņØ┤ ļ╣äĒĢ®ļ”¼ņĀüņØĖņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØäļ╣łļ▓łĒ׳ņ¦äĒ¢ēĒĢśņśĆĻ│Ā, ņĀäĒåĄņĀüĻ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖņØ┤ļĪĀņ£╝ļĪ£ļŖö ņäżļ¬ģņØ┤ ņ¢┤ļĀżņÜ┤ ĒśäņāüļōżņØ┤ ņåŹņČ£Ē¢łĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņØ┤ļŗż. ņśłļź╝ ļōżņ¢┤, ņŻ╝ņŗØņØä ļ¦żĻ░üĒĢśņŚ¼ ņ×ÉĻĖłņØä ĒÖĢļ│┤ĒĢ┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓ĮņÜ░, Ļ░£ņØĖĒł¼ņ×Éņ×ÉļōżņØĆ ĻĖ░ņŚģņØś ņ×¼ļ¼┤ ņāüĒā£ņÖĆ ņśüņŚģ ņĀäļ¦ØņØä ļČäņäØĒĢśņŚ¼ ļ¦żļ¦żĒĢĀ ņŻ╝ņŗØ ņóģļ¬®ņØä ņäĀņĀĢ ĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖĻ│Ā, ļ¦żņ×ģĻ░ĆĻ▓®ļ│┤ļŗż ĒĢśļØĮĒĢ£ ņŻ╝ņŗØņØĆ Ļ│äņåŹ ļ│┤ņ£ĀĒĢśĻ│Ā, ļ¦żņ×ģ Ļ░ĆĻ▓®ļ│┤ļŗż ņāüņŖ╣ĒĢ£ ņŻ╝ņŗØņØä ļ¦żĻ░üĒĢśļĀżļŖö Ļ▓ĮĒ¢źņØ┤ ņ׳ļŗż. ņØ┤ļŖö ĒĢ®ļ”¼ņĀü ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØ┤ļØ╝Ļ│Ā ļ│┤ĻĖ░ ņ¢┤ļĀĄĻ│Ā, ņĀäĒåĄņĀü Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖ ņØ┤ļĪĀņ£╝ļĪ£ ņäżļ¬ģĒĢśļŖöļŹ░ ĒĢ£Ļ│äĻ░Ć ņ׳ņŚłļŗż.
ĻĘĖļלņä£, Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖņ×ÉņÖĆ ņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖņ×ÉļōżņØĆ ĻĖłņ£Ąņŗ£ņןņØś ĒśäņāüļōżņØ┤ ņĀäĒåĄņĀüņØĖ Ēī©ļ¤¼ļŗżņ×äņ£╝ļĪ£ ņäżļ¬ģĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ¢┤ļĀĄļŗżļŖö ņé¼ņŗżņØä ņØĖņ¦ĆĒĢśĻ│Ā Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖņ£╝ļĪ£ ņäżļ¬ģĒĢśļĀżļŖö ņøĆņ¦üņ×äņØ┤ ņāØĻ▓╝ļŗż (Barberis and Thaler, 2002). Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖņØĆ Ē¢ēļÅÖĻ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖņØś ĒĢśņ£ä ĒĢÖļ¼Ėņ£╝ļĪ£ ĻĖłņ£ĄņŚÉ Ļ┤ĆļĀ©ļÉ£ ņØĖĻ░äņØś Ē¢ēĒā£ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ Ļ│ĄļČĆļōżļĪ£ ĻĄ¼ņä▒ļÉśņ¢┤ ņ׳ļŗż(Forbes, 2009). Ritter(2003)ņŚÉ ņØśĒĢśļ®┤, Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖņØĆ ĻĖłņ£Ąņŗ£ņןņØ┤ ļ╣äĒÜ©ņ£©ņĀü Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ņÖĆ ņé¼ļ×īļōżņØ┤ ĻĖłņ£Ą ļīĆĒĢ┤ņä£ ņ¢┤ļ¢╗Ļ▓ī ņāØĻ░üĒĢśĻ│Ā Ē¢ēļÅÖĒĢśļŖöņ¦Ćļź╝ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ĒĢśļŖö ĒĢÖļ¼ĖņØ┤ļØ╝Ļ│Ā ņĀĢņØśĒ¢łļŗż. ļŗżļźĖ Ēæ£Ēśäņ£╝ļĪ£, Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖņØĆ ņØĖĻ░ä ņŗ¼ļ”¼ĒĢÖ, ņé¼ĒÜīĒĢÖĻ│╝ ņØĖļźśĒĢÖņØä ļ░öĒāĢņ£╝ļĪ£ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļÉ£ ņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖņØ┤ļŗż(Shiller, 1998).
ņØ┤ņ▓śļ¤╝ņĀäĒåĄņĀüņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖņŚÉņä£ļŖöņØĖĻ░äņØäĒĢ®ļ”¼ņĀüņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņ×ÉļĪ£Ļ░äņŻ╝ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī Ē¢ēļÅÖ ņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņØĖĻ░äņØ┤ ĒĢŁņāü ĒĢ®ļ”¼ņĀüņØĖ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØä ĒĢśņ¦ĆļŖö ņĢŖļŖöļŗżĻ│Ā ņĀäņĀ£ĒĢśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż(Chen et al., 2017).
Arkes and Blumer(1985)ļŖö ļ¦żļ¬░ļ╣äņÜ®ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļź╝ ĻĖ░ņĪ┤ņŚÉ ņŗ£Ļ░ä, ļģĖļĀźĻ│╝ ļÅłņØ┤ Ēł¼ņ×ģļÉ£ Ēł¼ņ×ÉņŚÉ ņ¦ĆņåŹņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļģĖļĀź, ņŗ£Ļ░äĻ│╝ ļÅłņØä Ēł¼ņ×É ĒĢśļĀżļŖö Ļ▓ĮĒ¢źņØä ļ¦ÉĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ļØ╝Ļ│Ā ņĀĢņØśĒ¢łļŗż. ņé¼ļ×īļōżņØĆ ĻĖ░ Ēł¼ņ×ÉĒĢ£ ņŗ£Ļ░ä, ļģĖļĀź, ņ×ÉĻĖł ļō▒ Ēł¼ņ×ģļÉ£ņ×ÉņøÉļōżņØ┤ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņŚÉņ¦üņĀæņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣£ļŗżĻ│Ā ņŚ¼ļ¤¼ Ļ░Ćņ¦Ć ņŗżĒŚś Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ ĒåĄĒĢśņŚ¼ ņŻ╝ņןĒĢśņśĆļŗż. Ļ░ĆļĀ╣, ĒĢ£ ņŖżĒéżņŚ¼Ē¢ē ņŗżĒŚśņŚÉņä£, ņĀäĒåĄņĀü Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖ ņØ┤ļĪĀņØä ļö░ļź┤ņ×Éļ®┤ ļ¬©ļōĀ ņŗżĒŚś ņ░ĖņŚ¼ņ×ÉļōżņØĆ ļ»Ėņŗ£Ļ▒┤ņŖżĒéżņŚ¼Ē¢ēļ│┤ļŗżņŗĖĻ│ĀļŹöļ¦żļĀźņĀüņØĖņ£äņŖżņĮśņŖżĒéżņŚ¼Ē¢ēņØä ņäĀĒāØĒ¢łņ¢┤ņĢ╝ Ē¢łļŗż. ĻĘĖļ¤¼ļéś, ņśżņ¦ü 46%ņØś ņŗżĒŚś ņ░ĖņŚ¼ņ×Éļōżļ¦ī ņ£äņŖżņĮś ņŖżĒéż ņŚ¼Ē¢ēņØä ņäĀĒāØĒ¢łļŗż. ĻĘĖ ņØ┤ņ£ĀļŖö ņØ┤ļ»Ė ļ»Ėņŗ£Ļ▒┤ ņŖżĒéżņŚ¼Ē¢ēņŚÉ Ēł¼ņ×ģļÉ£ ļ¦ÄņØĆļ¦żļ¬░ļ╣äņÜ®ņØ┤ņ¦üņĀæņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņŗżĒŚś ņ░ĖņŚ¼ņ×ÉļōżņØś ņäĀĒāØņŚÉ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ņŻ╝ņŚłĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņØ┤ņŚłļŗż. ļśÉ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņ×ÉļōżņØĆ ļĀłņØ┤ļŗżņŚÉ ļģĖņČ£ļÉśņ¦Ć ņĢŖļŖö ļ╣äĒ¢ēĻĖ░ ņĀ£ņ×æ ĒöäļĪ£ņĀØĒŖĖļź╝ ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ļ¦żļ¬░ ļ╣äņÜ®ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņŗżĒŚśņØä ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņØ┤ ņŗżĒŚś ņŚÉņä£ ļ¬©ļōĀ Ļ░ĆņĀĢņØĆ ļÅÖņØ╝ĒĢśĻ│Ā, Ēł¼ņ×ÉĻ░Ć ņØ┤ļ»Ė ņØ┤ļŻ©ņ¢┤ņĪīļŗżļŖö Ļ░ĆņĀĢĻ│╝ ņĢäņ¦ü Ēł¼ņ×ÉĻ░Ć ņØ┤ļŻ©ņ¢┤ņ¦Ćņ¦Ć ņĢŖņĢśļŗżļŖö Ļ░ĆņĀĢņØś ņ░©ņØ┤ļź╝ ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ļ¦żļ¬░ ļ╣äņÜ® ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļź╝ ļ¬ģĒÖĢĒĢśĻ▓ī ņ×ģņ”ØĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņé¼ņĀä Ēł¼ņ×ÉĻ░Ć ņØ┤ļŻ©ņ¢┤ņĪīļŗżļŖö Ļ░ĆņĀĢņŚÉņä£ļŖö 85%ņØś ņŗżĒŚś ņ░ĖņŚ¼ņ×ÉļōżņØ┤ ĒöäļĪ£ņĀØĒŖĖ Ļ░£ļ░£ ņ¦ĆņåŹņØä ņäĀĒāØ ĒĢśņśĆĻ│Ā, Ēł¼ņ×ÉĻ░Ć ņĢäņ¦ü ņØ┤ļŻ©ņ¢┤ņ¦Ćņ¦Ć ņĢŖņĢśļŗżļŖö Ļ░ĆņĀĢņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņśżņ¦ü 17%ņØś ņŗżĒŚś ņ░ĖņŚ¼ņ×Éļōżļ¦ī ļĀłņØ┤ļŹöņŚÉ ļģĖņČ£ļÉśņ¦Ć ņĢŖļŖö ļ╣äĒ¢ēĻĖ░ Ļ░£ļ░£ ĒöäļĪ£ņĀØĒŖĖļź╝ ņ¦Ćņ¦ĆĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņØ┤ņ▓śļ¤╝ ņåīļ╣äņ×É Ē¢ēņ£ä, Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ņĀü ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢĻ│╝ ĻĖ░ĒāĆ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢ ļō▒ ņŚ¼ļ¤¼ ĒśäņāüļōżņŚÉņä£ ņØ┤ļ¤¼ĒĢ£ ļ¦żļ¬░ ļ╣äņÜ®ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļŖö ļ░£ņāØĒĢ£ļŗż(Putten et al., 2010). ĒŖ╣Ē׳ ņØ┤ļ¤¼ĒĢ£ ļ¦żļ¬░ļ╣äņÜ®ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļŖö ņØ┤ņØĄņØ┤ ņŗżĒśäļÉśļŖö Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ļ│┤ļŗż ņåÉņŗżņØ┤ ļ░£ņāØļÉśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŖö ņāüĒÖ®ņŚÉņä£ ļŹö ļ╣łļ▓łĒĢśĻ▓ī ļéśĒāĆļé£ļŗż(Tversky and Kahneman, 1981).
Haita-Falah(2017) ļśÉĒĢ£ ņé¼ļ×īļōżņØĆ ļ¦żļ¬░ ļ╣äņÜ® ņśżļźśņŚÉ ļ╣Āņ¦ĆļŖö Ļ▓ĮĒ¢źņØ┤ ņ׳ļŗżĻ│Ā ņŻ╝ņןĒ¢łļŗż. Rego et al.(2010)ļÅä ļ¦żļ¬░ ļ╣äņÜ® ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļŖö ņØĖĻ░äĻ┤ĆĻ│äņŚÉ ņ¦üņĀæņĀüņØĖ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣£ļŗżĻ│Ā ņŻ╝ņןĒ¢łļŗż. ĻĘĖļōżņØĆ ņŗ£Ļ░ä, ļģĖļĀź, ļÅł ļō▒ ņØĖĻ░äĻ┤ĆĻ│äņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ Ēł¼ņ×ÉļōżņØ┤ ĻĘĖ Ļ┤ĆĻ│ä ņ£Āņ¦ĆņØś ņżæņÜöĒĢ£ ļÅÖĻĖ░ļČĆņŚ¼Ļ░Ć ļÉ£ļŗżĻ│Ā ļģ╝ļ¼ĖņŚÉņä£ ņ¢ĖĻĖēĒ¢łļŗż(Rego et al., 2018). ņĢ×ņä£ Ēł¼ņ×ÉĻ░Ć ņØ┤ļŻ©ņ¢┤ņ¦ä Ļ▓ĮņÜ░, ņé¼ļ×īļōżņØĆ ĻĘĖ ĒöäļĪ£ņĀØĒŖĖĻ░Ć ļ¦łļ¼┤ļ”¼ ļÉśļÅäļĪØ Ļ│äņåŹ ņ¦äĒ¢ēĒĢśļĀżļŖö Ļ▓ĮĒ¢źņØ┤ ņ׳ļŗż(Putten et al., 2010). Putten et al.(2010) ņØĆ ŌĆ£Who throws good money after bad? Action vs. state orientation moderates the sunk cost fallacyŌĆØņŚÉņä£ ņØ┤ļ»Ė Ēł¼ņ×ÉĻ░Ć ņØ┤ļŻ©ņ¢┤ņ¦ä ĒöäļĪ£ņĀØĒŖĖņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ļŖö ĒöäļĪ£ņĀØĒŖĖļź╝ ņ¦ĆņåŹņŗ£ĒéżļĀżļŖö Ļ▓ĮĒ¢źņØ┤ ņ׳ļŗżĻ│Ā ņĀüņŗ£Ē¢łļŗż.
Garland and Newport(1991)ļŖö ļ¦żļ¬░ ļ╣äņÜ® ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļź╝ ļČäņäØĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ņä£ ļäż Ļ░£ņØś ņŗ£ļéśļ”¼ņśżļź╝ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśņśĆĻ│Ā, ĻĘĖļōżņØĆ ĒöäļĪ£ņĀØĒŖĖ ņ¦ĆņåŹņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņŚÉ ĻĖ░ Ēł¼ņ×ģļÉ£ ņ×ÉņøÉļōżņØ┤ ņ¦üņĀæņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ņżĆļŗżļŖö ņé¼ņŗżņØä ļ░£Ļ▓¼Ē¢łļŗż. ņé¼ļ×īļōżņØĆ ĒöäļĪ£ņĀØĒŖĖņŚÉ ņØ┤ļ»Ė Ēł¼ņ×ģļÉ£ ņ×ÉņøÉņØ┤ ļéŁļ╣äņÖĆ ņåÉņŗżļĪ£ ĒÅēĻ░ĆļÉśļŖö Ļ▓āņØä ņøÉĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖĻĖ░ņŚÉ ņŗżĒī©Ļ░Ć ņśłņāüļÉśļŖö ĒöäļĪ£ņĀØĒŖĖļź╝ Ļ│äņåŹ ņ¦äĒ¢ēĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓ĮĒ¢źņØ┤ ņ׳ļŗż(Arkes and Ayton, 1999; Keasey and Moon, 2000). Ēöäļ”¼ļō£ļ©╝ ļō▒ņØĆ ņ╗┤Ēō©Ēä░Ļ▓īņ×äņØä ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ļ¦żļ¬░ļ╣äņÜ® ņśżļźśļź╝ Ļ▓Ćņ”ØĒĢśņśĆļŖöļŹ░, ņ░ĖņŚ¼ņ×ÉļōżņØĆ ļåÆņØĆ ļ¦żļ¬░ļ╣äņÜ®ņØ┤ Ēł¼ņ×ģļÉ£ ņä¼ņŚÉ ļ©Ėļ¼╝ļĀżļŖö Ļ▓ĮĒ¢źņØ┤ ņ׳ņØīņØä ļ░£Ļ▓¼ĒĢśņśĆļŗż(Friedman et al., 2007).
ņåīļ╣äņ×ÉņŚÉĻ▓ī ļ¦żļ¬░ļ╣äņÜ®ņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØĖņŗØļÉśļŖö ĒÜīņøÉ Ļ░Ćņ×ģ ļ╣äņÜ®ņØĆ ņåīļ╣äņ×ÉņØś Ēā£ļÅäņÖĆ ņäĀĒāØņŚÉ ņ¦üņĀæņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣£ļŗż. ĒÜīņøÉĻ░Ćņ×ģļ╣äņÜ®ņØä ņ¦ĆļČłĒĢ£ ĒøäņŚÉ ņåīļ╣äņ×ÉņØś ņåīļ¦żņĀÉ ņäĀĒāØņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ Ēā£ļÅäļŖö ĒÖĢņŗżĒ׳ ļŗżļź┤ļŗż. ĒÜīņøÉ Ļ░Ćņ×ģļ╣äņÜ®ņØĆ ņåīļ╣äņ×ÉļōżņŚÉĻ▓ī ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņāüņĀÉņØä ļŹö ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢśĻ▓ī ĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓ĮĒ¢źņØ┤ ņ׳ļŗż(Dick and Lord 1998). Garland(1990)ļŖö ļ¦żļ¬░ļ╣äņÜ®ņØ┤ ĒöäļĪ£ņĀØĒŖĖļź╝ Ļ│äņåŹ ņ¦äĒ¢ēĒĢĀņ¦Ć ĒżĻĖ░ĒĢĀņ¦ĆņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņŚÉ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ņżä ņłś ņ׳ļŗżĻ│Ā ļ¬ģņŗ£Ē¢łļŗż. ĻĘĖļŖö ļśÉĒĢ£ ļ¦żļ¬░ļ╣äņÜ®ņØĆ ļ»ĖļלņØś ņłśņØĄņä▒ļ│┤ļŗżļÅä ļŹö ņČöĻ░ĆņĀü Ēł¼ņ×É Ļ▓░ņĀĢņŚÉ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ņżĆļŗżĻ│Ā ņŻ╝ņןĒ¢łļŗż. ļ¦żļ¬░ ļ╣äņÜ® ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņÖĆ Ļ┤ĆļĀ©ļÉ£ ĒöīļØ╝ņŖżĒŗ▒ ņśĘĻ░É Ļ░£ļ░£ ĒöäļĪ£ņĀØĒŖĖ ņ¦ĆņåŹ ļ░Å ņ£Āņ¦ĆņŚÉ Ļ┤ĆĒĢ£ ĒĢ£ ņŗżĒŚśņŚÉņä£ļÅä ļīĆļŗżņłśņØś ņ░ĖņŚ¼ņ×ÉļōżņØĆ ĒöäļĪ£ņĀØĒŖĖņØś ņ¦ĆņåŹņØä ņäĀĒāØĒ¢łļŖöļŹ░, ĻĘĖ ņØ┤ņ£ĀļŖö ĻĘĖļÅÖņĢłĒł¼ņ×ģļÉ£ņ×ÉņøÉņØ┤ļéŁļ╣äļĪ£ĒÅēĻ░ĆļÉśĻĖ░ļź╝ ņøÉĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņØ┤ņŚłļŗż (Arkes, 1996).
Tan and Yates(1995)ļŖöļ”¼ņĪ░ĒŖĖņäĀĒāØĻ│╝ĒĢĖļō£ĒÅ░Ēł¼ņ×É ņé¼ļĪĆļź╝ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ļ¦żļ¬░ļ╣äņÜ®ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļź╝ļČäņäØĒ¢łļŗż. ļ”¼ņĪ░ĒŖĖņäĀĒāØņŗżĒŚśņŚÉņä£56%ņØśņŗżĒŚśņ░ĖņŚ¼ņ×ÉĻ░Ć ļ¦żļ¬░ ļ╣äņÜ® ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļĢīļ¼ĖņŚÉ ņāüļīĆņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļŹ£ ņäĀĒśĖĒĢśļŖö ļ░öĒāÉ ņŚ¼Ē¢ēņØä ņäĀĒāØ Ē¢łĻ│Ā, ĒĢĖļō£ĒÅ░ Ēł¼ņ×ÉņŚÉ Ļ┤ĆĒĢ£ ņŗżĒŚśņŚÉņä£ļŖö ļ¦żļ¬░ ļ╣äņÜ® ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņŚÉ Ļ┤ĆĒĢ£ ņØ┤ļĪĀņØä ļ¬©ļź┤ļŖö 80%ņØś ĒĢÖņāØļōżņØ┤ ĻĖ░ Ēł¼ņ×ģļÉ£ ļ╣äņÜ® ļĢīļ¼ĖņŚÉ ņČöĻ░ĆņĀü ļ╣äņÜ®ņØä Ēł¼ņ×ģĒĢ┤ņä£ ĒöäļĪ£ņĀØĒŖĖļź╝ ņÖäņä▒ĒĢśļŖö ņäĀĒāØņØä Ē¢łļŗż.
Gourville and Soman(1998)ņØ┤ ļČäņäØĒĢ£ ņ×ÉļŻīņŚÉ ļö░ļź┤ļ®┤, 2ļģäņŚÉ ĒĢ£ļ▓łņö® ļ®żļ▓äņēĮ ļ╣äņÜ®ņØä ņ¦ĆļČłĒĢśļŖö ĒŚ¼ņŖżĒü┤ļ¤Į ņØ┤ņÜ®ņ×ÉļōżņØĆ ļ®źļ▓äņēĮ ļ╣äņÜ®ņØä ņ¦ĆļČłĒĢśļŖö ļŗ¼ņŚÉļŖö ĒŚ¼ņŖżĒü┤ļ¤ĮņØä ļŗżļźĖ ļŗ¼ļ│┤ļŗż Ēø©ņö¼ ļŹö ļ¦ÄņØ┤ ņØ┤ņÜ®Ē¢łļŗż. ĻĘĖļōżņØĆ ļ¦żļ¬░ļ╣äņÜ®ņØ┤ ņåīļ╣äņ×ÉņØś Ē¢ēļÅÖņŚÉ ņ¦üņĀæņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣£ļŗżĻ│Ā ņŻ╝ņןĒ¢łļŗż. ļ¦żļ¬░ ļ╣äņÜ® ņśżļźśļŖö ņŖżĒżņĖĀ ļČäņĢ╝ņŚÉņä£ļÅä ļ░£Ļ▓¼ ļÉ£ļŗż. KeeferļŖö ļ»ĖĻĄŁ ļ®öņØ┤ņĀĆļ”¼ĻĘĖ ņäĀņłśļōżņØś ņČ£ņĀäņŗ£Ļ░äņØ┤ ļ¦żļ¬░ ļ╣äņÜ® ņśżļźśņŚÉ Ļ░ĢĒĢśĻ▓ī ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ░øļŖöļŗżĻ│Ā Ē¢łņ£╝ļ®░(Keefer, 2015), NFL ņäĀņłśļōżņØśņČ£ņĀäņŗ£Ļ░äļÅäļ¦żļ¬░ļ╣äņÜ®ņśżļźśņŚÉņśüĒ¢źņØäļ░øņ£╝ļ®░, ņäĀņłśļōżņØśņĀĢĒÖĢĒĢ£ Ļ▓ĮĻĖ░ ņŗżņĀüĻ│╝ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝Ļ░Ć ļ¦żļ¬░ļ╣äņÜ®ņśżļźśļź╝ ņĀ£Ļ▒░ĒĢśņ¦ĆļŖö ļ¬╗ĒĢ£ļŗżĻ│Ā ņŻ╝ņןĒ¢łļŗż(Keefer, 2018).
ļé«ņØĆ Ļ▓Įļ¦ż ņŗ£ņ×æ Ļ░ĆĻ▓®ņØĆ ļ¦ÄņØĆ Ļ▓Įļ¦ż ņ░ĖņŚ¼ņ×Éļź╝ ņ£ĀļÅäĒĢ£ļŗż. ņ┤łĻĖ░ņŚÉ ļé«ņØĆ Ļ░ĆĻ▓® ļĢī ņ×ģņ░░ ņ░ĖņŚ¼ļŖö ļ¦żļ¬░ ļ╣äņÜ®ņØ┤ ļÉśļŖö Ļ▓ĮĒ¢źņØ┤ ņ׳Ļ│Ā ņČöĻ░ĆņĀü Ēł¼ņ×Éļź╝ ņØ┤ļüīņ¢┤ļéĖļŗż. ņ┤łĻĖ░ ņ░ĖņŚ¼ņ×ÉļŖö ņ¦ĆņåŹņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ×ģņ░░ņŚÉ ņ░ĖņŚ¼ĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓ĮĒ¢źņØ┤ ņ׳Ļ│Ā ļéÖņ░░Ļ░ĆĻ▓®ņØä ņś¼ļ”¼ļŖö Ļ▓ĮĒ¢źņØ┤ ņ׳ļŗż(Ku et al., 2006). Ho et al.(2018)ļŖö ņ×ÉļÅÖņ░© ņé¼ņÜ® ļ╣łļÅäļź╝ ļČäņäØĒĢśņŚ¼ ļ¦żļ¬░ ļ╣äņÜ® ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļź╝ ņ×ģņ”ØĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņ×ÉļÅÖņ░© ņåīņ£ĀņŻ╝ļōżņØĆ ņŗĀņ░©ļź╝ ĻĄ¼ņ×ģĒĢ£ Ēøä ņĄ£ņ┤ł 2ļģäĻ░ä ņ░©ļź╝ ļ¦żņÜ░ ņ×ÉņŻ╝ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśļŖöļŹ░, ĻĘĖ ņØ┤ņ£ĀļŖö ļ¦żļ¬░ ļ╣äņÜ® ļĢīļ¼ĖņØ┤ļØ╝Ļ│Ā Ļ░ĢņĪ░Ē¢łļŗż. ļ¦żļ¬░ļ╣äņÜ®ņØ┤ ņé¼ļ×īļōżņØśļ©Ėļ”¼ņåŹĻ│äņĀĢņŚÉņ¦üņĀæņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣£ļŗżĻ│Ā ņŻ╝ņןĒ¢łļŗż.
Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖņŚÉņä£ņĀĢņØśĒĢśļŖöļ¦żļ¬░ļ╣äņÜ®ņØ┤ļ×Ć ņØ┤ļ»ĖĒł¼ņ×ģļÉ£ņŗ£Ļ░ä, ļģĖļĀźĻ│╝ ņ×ÉĻĖłļō▒ņØäņØśļ»ĖĒĢ£ļŗż. ņØĖĻ░äņØ┤ĒĢ®ļ”¼ņĀüĒ¢ēņ£äņ×ÉļØ╝ļ®┤ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØäĒĢśĻ▒░ļéśņäĀĒāØņØä ĒĢĀĻ▓ĮņÜ░ļ»ĖļלņØśļ╣äņÜ®Ļ│╝ĒÄĖņØĄļō▒ņØäĻĖ░ņżĆņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒĢ┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī ņé¼ļ×īņØĆ ĒĢŁņāü ĒĢ®ļ”¼ņĀüņØĖņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØäĒĢśļŖöņŻ╝ņ▓┤Ļ░ĆņĢäļŗłļ»ĆļĪ£, Ļ│╝Ļ▒░ņŚÉļ░£ņāØĒĢ£ļ¦żļ¬░ļ╣äņÜ®ņØ┤ ļ»Ėļלļź╝ņ£äĒĢ£ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņŚÉņśüĒ¢źņØäļ»Ėņ╣śĻĖ░ļÅäĒĢśļŖöļŹ░, ņØ┤ļź╝Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖņŚÉņä£ļŖö ļ¦żļ¬░ļ╣äņÜ®ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļØ╝Ļ│ĀĒĢ£ļŗż. ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņŚÉņä£ļÅäļ¦żļ¬░ļ╣äņÜ®ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļĪ£ ņØĖĒĢśņŚ¼, ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņ×ÉļōżņØ┤ļ╣äĒĢ®ļ”¼ņĀüņØĖņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØäĒĢśļŖöĻ▓ĮņÜ░Ļ░Ć ņ׳ļŗżĻ│Ā ņØśņŗ¼ļÉ£ļŗż. ļ│Ė ļģ╝ļ¼ĖņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņäżļ¼Ėņ¦Ćļ▓ĢĻ│╝ ņé¼ļĪĆņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļź╝ ĒåĄĒĢśņŚ¼ ņĢ×ņä£ ņ¢ĖĻĖēĒĢ£ ļ¦żļ¬░ ļ╣äņÜ® ĒÜ©Ļ│╝Ļ░Ć ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņŚÉņä£ļÅä ņĪ┤ņ×¼ĒĢśĻ│Ā ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ│żļŖöņ¦Ć ļČäņäØĒĢĀ ņśłņĀĢņØ┤ļŗż.
Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖ ņØ┤ļĪĀ ņżæ Ļ░Ćņן ņØ╝ļ░śņĀüņØ┤Ļ│Ā ņżæņÜöĒĢ£ ĒśäņāüņØ┤ļ®░ ļ¦żņØ╝ ļ▓īņ¢┤ņ¦ĆļŖö ņØ╝ņżæņŚÉ ĒĢśļéśĻ░Ć ņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦ü ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņØ┤ļŗż (Kahneman, 2011). ņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦ü ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļŖö ņØĖņ¦ĆĒÄĖĒ¢źņØś ĒĢ£ ĒśĢĒā£ļĪ£ ņé¼ļ×īļōżņØ┤ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØä ĒĢĀ ļĢī ņĀ£Ļ│ĄļÉ£ ņ┤łĻĖ░ ņĀĢļ│┤ņŚÉ ņØśņ¦ĆĒĢśĻ▓ī ļÉśļŖö ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņØ┤ļŗż. ņé¼ļ×īļōżņØĆ ļČłĒÖĢņŗżņä▒ ĒĢśņŚÉņä£ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØä ĒĢĀ ļĢī ļ¬©ĒśĖĒĢ©ņØä ņżäņŚ¼ņżä ĻĖ░ņżĆņĀÉņØä ņ░ŠļŖö Ļ▓ĮĒ¢źņØ┤ ņ׳Ļ│Ā ĻĘĖ ĻĖ░ņżĆņĀÉņØä ņłśņĀĢĒĢśņŚ¼ ņĄ£ņóģ Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØä ĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓ĮĒ¢źņØ┤ ņ׳ļŗż. ņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦ü ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļŖö ņŗżņāØĒÖ£Ļ│╝ Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ĒÖ£ļÅÖņŚÉ ņżæņÜöĒĢ£ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣£ļŗż(Fiske and Taylor, 1991; Northcraft and Neale, 1987; Mussweiler et al., 2000). ņ”ē, ņé¼ļ×īļōżņØĆ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢĻ│╝ņĀĢņŚÉņä£ ņ£ĀņÜ®ĒĢ£ ņĀĢļ│┤Ļ░Ć ņŚåĻ▒░ļéś ļČłĒÖĢņŗżĒĢ£ ņāüĒÖ®ņŚÉņä£ ņČöņĀĢņØä ĒĢ┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢĀ Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ņ░ĖņĪ░ņĀÉļōżņØś ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ░øļŖöļŗż. Ļ░£ņØĖņØ┤ļéś ĻĘĖļŻ╣ ļ¬©ļæÉ ņØ┤ Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ĻĖ░ņżĆņĀÉņØś ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ░øļŖöļŗż (Whyte and Sebenius, 1997). Wright and Anderson(1989)ņØĆ ņØĖĻ░äņØś ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņŚÉ ņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦ü ĒÜ©Ļ│╝Ļ░Ć ņżæņÜöĒĢ£ ņŚŁĒĢĀņØä ĒĢ£ļŗżĻ│Ā ņŚ¼ļ¤¼ ņŗżĒŚśņØä ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ņ×ģņ”ØĒ¢łļŗż.
ņ╣┤ļäłļ©╝(Kahneman)ĻĄÉņłśļŖö 2011ļģäņŚÉ ņČ£ĒīÉĒĢ£ ĻĘĖņØś ņ▒ģ <Thinking, Fast and Slow>ņŚÉņä£ ņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦ü ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļź╝ ņäżļ¬ģĒ¢łļŗż. ĻĘĖļŖö ņāīĒöäļ×Ćņŗ£ņŖżņĮö Ļ│╝ĒĢÖĻ┤ĆņŚÉņä£ ĒĢ┤ņāü ĻĖ░ļ”ä ņ£ĀņČ£ļĪ£ ņØĖĒĢ£ ĒÖśĻ▓ĮņśżņŚ╝ņØä ņ▓śļ”¼ĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ£ ļ¬©ĻĖłņØä ņ¦äĒ¢ē ĒĢĀļĢī ļ░£ņāØĒĢ£ņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦üĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļź╝ ļČäņäØĒ¢łļŗż. ĒŖ╣ļ│äĒĢ£ ĻĖ░ļČĆ ĻĖ░ņżĆņĢĪņØ┤ ņŚåņØäļĢī ļ░®ļ¼Ėņ×ÉļōżņØ┤ ĻĖ░ļČĆĒĢ£ ĒÅēĻĘĀ ĻĖ░ļČĆņĢĪņØĆ Ļ░£ņØĖļŗ╣ 64ļČłņØ┤ņŚłļŗż. ĻĘĖļ¤¼ļéś, ĻĖ░ļČĆ ĻĖ░ņżĆņĢĪņØä 5ļČłļĪ£ ņĀĢĒĢ┤ļåōņ×É Ļ░£ņØĖļŗ╣ ĻĖ░ļČĆņĢĪņØĆ 20ļČłņØ┤ņŚłĻ│Ā, ĻĖ░ļČĆ ĻĖ░ņżĆņĢĪņØä 400ļČłļĪ£ ņĀĢĒĢ┤ļåōņ×É Ļ░£ņØĖļŗ╣ ĒÅēĻĘĀ ĻĖ░ļČĆņĢĪņØĆ 143ļČłņØ┤ņŚłļŗż. ņØ┤ ņŗżĒŚśņŚÉņä£ļÅä ļéśĒāĆļé¼ļō»ņØ┤ ņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦ü ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļŖö ņÜ░ļ”¼ ņŻ╝ņ£äņŚÉ ļČäļ¬ģĒĢśĻ▓ī ņĪ┤ņ×¼ĒĢ£ļŗż(Kahneman, 2011).
Tversky and Kahneman(1974)ņØĆ ņé¼ļ×īļōżņØ┤ ņČöņĀĢņØä ĒĢĀ ļĢī ņĄ£ ņ┤ł Ļ░ÆņØä ļ░öĒāĢņ£╝ļĪ£ ņČöņĀĢņØä ĒĢśļ®░, ņŗ£ņ×æņĀÉņØĆ ļ¦łņ¦Ćļ¦ē Ļ▓░ņĀĢņŚÉ ņ¦üņĀæņĀü ņØĖ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣£ļŗżĻ│Ā ņŻ╝ņןĒ¢łļŗż. ņĀĆņ×ÉļōżņØĆ ļśÉĒĢ£ ņé¼ļ×īļōżņØ┤ ņØśņé¼ Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØä ļŗ©ņł£ĒÖöĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ņä£ Ē£┤ļ”¼ņŖżĒŗ▒ņŖżļéś ņ¦üĻ┤ĆņØä ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓Į Ē¢źņØ┤ ņ׳ĻĖ░ņŚÉ ņ┤łĻĖ░ ņĀĢļ│┤ļŖö ĒøäņåŹ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņŚÉ ņ¦üņĀæņĀüņØĖ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ņżĆļŗżĻ│Ā ņŻ╝ņןĒ¢łļŗż. ņØ┤ļōżņØĆ Ļ│Āļō▒ĒĢÖĻĄÉ ĒĢÖņāØ ļæÉ ĻĘĖļŻ╣ņØä ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņŗżĒŚśņØä ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. 8ņŚÉņä£ 1Ļ╣īņ¦Ć ņżäņ¢┤ļō£ļŖö ņł½ņ×ÉļōżņØś Ļ│▒ņØä ņČöņĀĢĒĢ£ ņżæĻ░ä Ļ░ÆĻ│╝ 1ņŚÉņä£ 8ļĪ£ ļŖśņ¢┤ļéśļŖö ņł½ņ×ÉļōżņØś Ļ│▒ņØä ņČöņĀĢĒĢ£ ņżæĻ░ä Ļ░ÆņØä ļ╣äĻĄÉĒĢśļŖö ņŗżĒŚśņØ┤ņŚłļŗż. ņ▓½ļ▓łņ¦Ė ņ╝ĆņØ┤ņŖżņØś ņČöņĀĢ ņżæĻ░äĻ░ÆņØĆ 2,250ņØ┤ ņŚłĻ│Ā, ļæÉļ▓łņ¦Ė ņ╝ĆņØ┤ņŖżņØś ņČöņĀĢ ņżæĻ░äĻ░ÆņØĆ 512ļĪ£ ĻĘĖ ņ░©ņØ┤ļŖö ļ¦żņÜ░ ņ╗Ėļŗż. ļśÉ ļŗżļźĖ ņŗżĒŚśņØĆ ņĀäņäĖĻ│ä ĻĄŁĻ░Ć ņłśņŚÉņä£ ņĢäĒöäļ”¼ņ╣┤ ĻĄŁĻ░Ć ņłśĻ░Ć ņ░©ņ¦ĆĒĢśļŖö ļ╣äņ£©ņØä ņČöņĀĢĒĢśļŖö ņŗżĒŚśņØ┤ņŚłļŗż. ņ┤łĻĖ░ņŚÉ 10%ļź╝ ņĀ£ņŗ£ ļ░øņØĆ ĻĘĖļŻ╣ņØĆ ņČöņĀĢņ╣śļź╝ 25%ļĪ£ ņĀ£ņŗ£Ē¢łĻ│Ā, ņ┤łĻĖ░Ļ░ÆņØä 65%ļĪ£ ņĀ£ņŗ£ ļ░øņØĆĻĘĖļŻ╣ņØĆ 45%ļź╝ņČöņĀĢņ╣śļĪ£ ņĀ£ņŗ£Ē¢łļŗż. ļģ╝ļ¼ĖņØĆņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦üĒÜ©Ļ│╝ ļĢīļ¼ĖņŚÉ ņ┤łĻĖ░ ņŗ£ņ×æĻ░ÆņØ┤ ļŗżļź┤ļ®┤ ļŗżļźĖ ņČöņĀĢĻ░ÆņØ┤ ņĀ£ņŗ£ļÉ£ļŗżĻ│Ā ņŻ╝ņןĒ¢łļŗż.
Northcraft and Neale(1987)ņØĆņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦üĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļź╝ļČĆļÅÖņé░Ļ░ĆĻ▓®ņČöņĀĢņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ×ģņ”ØĒ¢łļŗż. ņØ┤ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉļö░ļź┤ļ®┤, ņĢäļ¦łņČöņ¢┤ļéśņĀäļ¼ĖĻ░ĆļéśļČĆļÅÖņé░Ļ░ĆĻ▓®ņČöņĀĢņØä ĒĢĀļĢīļéśņŚ┤ļÉ£ļČĆļÅÖņé░ĻĖ░ņżĆĻ░ĆņØśņśüĒ¢źņØäļ░øļŖöļŗżĻ│Āļ¬ģņŗ£ļÉśņ¢┤ņ׳ļŗż. ņĀĆņ×ÉļōżņØĆ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢ Ē£┤ļ”¼ņŖżĒŗ▒Ļ│╝ ĒÄĖĒ¢źņØ┤ ņØĖĻ░äļōżņØś ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢĒ¢ēĒā£ļź╝ņØ┤ĒĢ┤ĒĢśļŖöļŹ░ ņżæņÜöĒĢ£ņŚŁĒĢĀņØäĒĢ£ļŗżĻ│Āļ¬ģņŗ£Ē¢łļŗż. ņŚźņ╗żļ¦üĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļŖöņØ╝ļ│ĖĻ│╝ļ»ĖĻĄŁņØśņŻ╝ņŗØņŗ£ņן ņČöņäĖļČäņäØņŚÉņä£ļÅä ļéśĒāĆļé£ļŗż. ņØ╝ļ│ĖĻ│╝ ļ»ĖĻĄŁņØś ĻĖ░Ļ┤Ć Ēł¼ņ×Éņ×É ņāüļŗ╣ņłśļŖö ņØ╝ļ│Ė ņŻ╝ņŗØņŗ£ņןņØĆ ļ»ĖĻĄŁ ņŻ╝ņŗØņŗ£ņןņØś ļ│ĆĒÖöļōżņŚÉ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ░øļŖöļŗżĻ│Ā ļ»┐ļŖöļŗż. ĻĘĖļōżņØĆ ļ»ĖĻĄŁ ņŻ╝ņŗØ ņŗ£ņןņØś Ļ░ĆĻ▓®ļ│ĆĒÖöĻ░Ć ņØ╝ļ│Ė ņŻ╝ņŗØ ņŗ£ņןņØś Ļ░ĆĻ▓®ļ│ĆļÅÖņŚÉ ņżæņÜöĒĢ£ ņŚŁĒĢĀņØä ĒĢ£ļŗżĻ│Ā ņāØĻ░üĒĢ£ļŗż. (Shiller et al., 1996).
Mussweiler and Strack(2000)ļŖö ņ░© ļĖīļ×£ļō£ņÖĆ ņŗĀņ░© Ļ░ĆĻ▓® ņČöņĀĢņØä ĒĢśļŖö ņŗżĒŚśņØä ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦ü ĒÜ©Ļ│╝Ļ░Ć ņĪ┤ņ×¼ĒĢ£ļŗżļŖö ņé¼ņŗżņØä ņ×ģņ”ØĒ¢łļŗż. Ariely and Simonson(2003)ļÅä ņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦ü ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļź╝ ņŚ¼ļ¤¼ ņé¼ļĪĆļź╝ ļōżņ¢┤ ņ”Øļ¬ģĒ¢łļŗż. Ļ░ĆĻ▓®ĒśæņāüņŚÉņä£ ņĄ£ņ┤ł ņĀ£ņŗ£ Ļ░ĆĻ▓®ņØĆ ļ¦żņÜ░ ņżæņÜöĒĢśļŗż. ĻĖ░ņżĆ Ļ░ĆĻ▓®ņØ┤ Ēśæņāü ĻĖ░Ļ░ä ļÅÖņĢł ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣śĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņØ┤ļŗż. ņØ╝ļ░ś ĒśæņāüņŚÉņä£ļÅä ņĄ£ņ┤ł ņĀ£ņŗ£ ņśżĒŹ╝ļōżņØ┤ ĒśæņāüņŚÉ ļ¦żņÜ░ Ļ░ĢļĀźĒĢ£ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ņżĆļŗż. ņÖ£ļāÉĒĢśļ®┤, ņāüļīĆļ░®ņŚÉņä£ ņĀ£ņŗ£ĒĢśļŖö ņ╣┤ņÜ┤Ēä░ ņśżĒŹ╝ļōżņØĆ ņĄ£ņ┤łņŚÉ ņĀ£ņŗ£ļÉ£ ņśżĒŹ╝ļōżņØä ĻĖ░ņżĆņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĀ£ņŗ£ļÉśĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņØ┤ļŗż. ļśÉĒĢ£, ņś©ļØ╝ņØĖ Ļ▓Įļ¦żņŚÉņä£ļÅä Ļ▓Įļ¦ż ņ░ĖņŚ¼ņ×ÉļōżņØĆ ĒīÉļ¦żņ×ÉĻ░Ć ņäżņĀĢĒĢ£ ņĄ£ņ┤ł ņ×ģņ░░ Ļ░ĆĻ▓®ņĀĢļ│┤ņŚÉ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ░øļŖöļŗż. ņĪ░ņé¼ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ņŚÉ ļö░ļź┤ļ®┤, ņ┤łĻĖ░ Ļ▓Įļ¦ż ņŗ£ņ×æ Ļ░ĆĻ▓®ņØ┤ ļé«ņØäņłśļĪØ ļ¦ÄņØĆ Ļ▓Įļ¦ż ņ░ĖņŚ¼ņ×ÉļōżņØ┤ Ļ▓Įļ¦żņŚÉ ņ░ĖņŚ¼ĒĢ£ļŗż. Ļ▒░ĻĖ░ņŚÉ ļŹöĒĢśņŚ¼, Ļ▓Įļ¦ż ņ┤łĻĖ░ņØś ļé«ņØĆĻ░ĆĻ▓®ļōżņØĆļ¦żļ¬░ļ╣äņÜ®ņØäļ░£ņāØņŗ£ĒéżĻ│Ā, ņé¼ļ×īļōżņØäĻ░Ćņ╣śĒīÉļŗ©ņ£╝ļĪ£ļČĆĒä░ ļ®Ćņ¢┤ņ¦ĆĻ▓ī ĒĢ£ļŗż(Ariely and Simonson, 2003; Ku et al., 2006).
ņŻ╝ņŗØ Ēł¼ņ×Éņ×ÉļōżņØĆ ļ│ĖņØĖļōżņØ┤ ņäżņĀĢĒĢ£ Ļ░ĆĻ▓® ņĢłņŚÉņä£ ņŻ╝ņŗØ Ļ▒░ļלļź╝ ņ¦æņżæĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓ĮĒ¢źņØ┤ ņ׳ļŗż. ņ×Éļ│ĖĻ░ĆļōżņØĆ ņ¦ĆņĀĢĒĢ£ Ļ░ĆĻ▓®ļ│┤ļŗż ļé«ņØĆ Ļ░ĆĻ▓®ņŚÉ ņŻ╝ņŗØņØä ņé¼Ļ│Ā ņ¦ĆņĀĢĒĢ£ Ļ░ĆĻ▓®ļ│┤ļŗż ļåÆņØä ļĢī ņŻ╝ņŗØņØä ļ¦żĻ░üĒĢ£ļŗż. (Verousis and Gwilym, 2014). ĻĖłņ£ĄĻĖ░Ļ┤ĆļōżņØś Ļ▒░ņŗ£Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖņĀü ņĀäļ¦ØļōżņØĆ ĻĖ░ņĪ┤ņŚÉļ”¼ņä£ņ╣śĻĖ░Ļ┤ĆļōżņŚÉņä£ļ░£Ēæ£ĒĢ£ņĀäļ¦Øņłśņ╣śļōżņØäĻĖ░ļ│Ėņ£╝ļĪ£ņ×æņä▒ļÉ£ļŗż. ņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦üĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļŖöļ»ĖĻĄŁĻ│╝ņ£Āļ¤ĮņØśĻ▒░ņŗ£Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖņĀü ņśłņĖĪņ╣śļź╝ĻĖłņ£ĄĻĖ░Ļ┤ĆļōżņØ┤ ņĀäļ¦Ø ĒĢĀļĢīļÅä ļéśĒāĆļé£ļŗż(Chang and Chou, 2018). Liao et al.(2013)ņØĆ ļīĆļ¦ī ņŻ╝ņŗØĒł¼ņ×Éņ×ÉļōżņØĆ ņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦ü ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņŚÉ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ņ¦üņĀæņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ░øļŖöļŗżĻ│Ā ņŻ╝ņןĒ¢łļŗż. IPO Ļ░ĆĻ▓®ņØäņĀĢĒĢĀļĢī, ņżæĻĄŁĒł¼ņ×Éņ×ÉļōżņØĆņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦üĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļĢīļ¼ĖņŚÉ ņ¢ĖļŹöļØ╝ņØ┤Ēä░ļōżņØ┤ ņĀ£ņŗ£ĒĢ£ ņĄ£ņ┤ł Ļ░ĆĻ▓®ņØä ņ░ĖņĪ░ĒĢ┤ņä£ IPO ņ░ĖņŚ¼ Ļ░ĆĻ▓®ņØä ņĀĢĒĢ£ļŗżĻ│Ā Ļ░ĢņĪ░Ē¢łļŗż. ņŗ£Ļ░üņĀü ņł½ņ×ÉņĀü ĻĖ░ņżĆļōżņØ┤ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢ Ļ│╝ņĀĢĻ│╝ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝Ļ░ÆņŚÉņ¦üņĀæņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ņśüĒ¢źņØäņŻ╝ļŖöĻ▓ĮņÜ░ļŖöļ╣łļ▓łĒĢśļŗż(Cho et al., 2017).
ņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦ü ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļŖö ļ▓ĢņĀĢņŚÉņä£ļÅä ļéśĒāĆļé£ļŗż. Englich et al.(2005)ņØĆ Ļ▓Ćņé¼ņØś ņÜöĻĄ¼Ļ░Ć ĒīÉņé¼ņØś ĒīÉĻ▓░ņŚÉ ņ¦üņĀæņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣£ļŗżĻ│Ā ņŻ╝ņןĒ¢łļŗż. ļśÉĒĢ£, Ļ▓Ćņé¼ņØś ņÜöĻĄ¼ļŖö ļ│ĆĒśĖņé¼ņØś ļ│ĆļĪĀņŚÉļÅä ņśüĒ¢źņØä ņżĆļŗżĻ│Ā Ļ░ĢņĪ░Ē¢łļŗż. Englich and Mussweiler(2001)ļŖö Ļ▓Ćņé¼ņØś ņĄ£ņ┤ł ĻĄ¼ĒśĢņØĆ ĒīÉņé¼ņØś ņØśĻ▓¼ņŚÉ ņ¦üņĀæņĀüņØĖ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ņżĆļŗżĻ│Ā ļ░ØĒśöļŗż.
ņāüĻĖ░ ļé┤ņÜ®ļōżņØä ņĀĢļ”¼ĒĢśņ×Éļ®┤, ņé¼ļ×īļōżņØś ļ©Ėļ”┐ņåŹņŚÉ ĒŖ╣ņĀĢĒĢ£ ņĀĢļ│┤, ņØ┤ļ»Ėņ¦Ć Ēś╣ņØĆ ņłśņ╣śĻ░Ć Ļ░üņØĖļÉśļ®┤, ņé¼ļ×īļōżņØĆ ĻĘĖĻ▓āņØä ļ▓Śņ¢┤ļéś ņ×Éņ£ĀļĪ£ņÜ┤ ĒīÉļŗ©ņØä ļé┤ļ”¼ĻĖ░ ņ¢┤ļĀĄĻ│Ā ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņĀĢļ│┤ ļō▒ņØä ĻĖ░ņżĆņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒīÉļŗ©ņØä ĒĢśĻ▓ī ļÉśļŖöļŹ░ ņØ┤ļź╝ Ē¢ēļÅÖ ņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖņŚÉņä£ ņŚźņ╗żļ¦ü ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļØ╝Ļ│Ā ĒĢ£ļŗż. ņØ┤ Ļ░ÖņØĆ ņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦ü ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļŖö ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņŚÉņä£ ļ╣łļ▓łĒĢśĻ▓ī ļéśĒāĆļé£ļŗżĻ│Ā ņČöņĀĢļÉ£ļŗż. ļ│Ė ļģ╝ļ¼ĖņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņØ┤ Ļ░ÖņØĆ ĒśäņāüņØ┤ ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņāü ņŗżņĀ£ ņĪ┤ņ×¼ĒĢśļŖöņ¦Ć ņŚ¼ļČĆņÖĆ ņ¢┤ļ¢ż ņśüĒ¢źņØä ņŻ╝ņŚłļŖöņ¦Ćļź╝ ļČäņäØĒĢĀ ņśłņĀĢņØ┤ļŗż.
ņØ┤ ļģ╝ļ¼ĖņØĆ ļæÉĻ░Ćņ¦Ć ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ ļ¬®ņĀüņØä Ļ░Ćņ¦ĆĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż. ĒĢśļéśļŖö Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖ ņØ┤ļĪĀļōżņØä ņä£ņłĀņØæļŗĄĻ│╝ ņäżļ¼ĖņØæļŗĄņŚÉ ņĀüņÜ®ĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤Ļ│Ā, ļśÉ ļŗżļźĖ ĒĢśļéśļŖö ņäżļ¼Ė ņ░ĖņŚ¼ņ×ÉļōżĻ│╝ ņä£ņłĀņØæļŗĄ ņ░ĖņŚ¼ņ×ÉļōżņØś ņØæļŗĄņØä ļČäņäØĒĢśĻ│Ā, ĻĘĖņØæļŗĄņŚÉļö░ļźĖņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢļōżņØ┤ĒĢ®ļ”¼ņĀüņØĖ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØ┤ņŚłļŖöņ¦ĆņČöļĪĀĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ļŗż.
Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖ ņØ┤ļĪĀļōżņØĆ ņØĖĻ░äņØś ļ¬©ņł£ņĀüņØĖ ņŗ¼ļ”¼ņŚÉ Ļ┤ĆĒĢ£ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļōżņØä ĒåĄĒĢśņŚ¼ ļ░£ņĀäļÉśņŚłļŗż. ļ│Ė ļģ╝ļ¼ĖņØĆ ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ĻĖ░ņŚģ, ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņ×ÉļōżņØä ļīĆņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņäżļ¼ĖņĪ░ņé¼ņÖĆ ņé¼ļĪĆ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļź╝ ĒåĄĒĢ┤ņä£ ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ ļ░Å ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņĀäļ¼ĖĻ░ĆļōżņØ┤ ņäĀĒāØĒĢ£ ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£ĄĻ┤ĆļĀ© ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢļōżņØä ļČäņäØĒĢśĻ│Āņ×É ĒĢ£ļŗż. ņØ┤ļź╝ ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ņäĀĒāØĒĢ£ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢļōżņØ┤ ļ╣äĒĢ®ļ”¼ņĀü ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØĆ ņĢäļŗłņŚłļŖöņ¦Ćļź╝ ņĢīņĢäļ│┤Ļ│Ā, Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖ ņØ┤ļĪĀļōżļĪ£ ņäżļ¬ģ Ļ░ĆļŖźĒĢ£ņ¦Ćļź╝ ņé┤ĒÄ┤ļ│┤Ļ│Āņ×É ĒĢ£ļŗż.
ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£ĄņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņ×ÉļŖöĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ĻĖ░ņŚģņØśĻ▓Įņśüņ¦äĻ│╝ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ąļŗ┤ļŗ╣ņ×ÉļōżņØ┤ĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņŚÉ ļ│Ė ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļŖö ĻĘĖļōżņØś Ļ┤ĆņĀÉņŚÉņä£ ņ¦äĒ¢ēļÉśņ¢┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢśļ®░ Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖņĀü Ļ┤ĆņĀÉņŚÉņä£ ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņŚÉ Ļ┤ĆĒĢ£ ļČäņäØņØä ĒĢśĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņŚÉ ņ¦łņĀü ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļ░®ļ▓ĢņØ┤ ļ│Ė ļģ╝ļ¼ĖņØś ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļ░®ļ▓Ģņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ĀņÜ®ĒĢśļŗżĻ│Ā ĒīÉļŗ©ļÉ£ļŗż. ņ¦łņĀü ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļŖöņŻ╝Ļ┤ĆņĀü┬ĘĒĢ┤ņäØņĀüņØĖņŗØļĪĀņŚÉĻĘ╝Ļ▒░ļź╝ļæÉĻ│Ā, ļÉśļÅäļĪØņØĖņ£äņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ņĪ░ņ×æļÉśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņØĆ ņ×ÉņŚ░ņŖżļ¤¼ņÜ┤ ņāüĒÖ®ņŚÉņä£ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļīĆņāü ņŖżņŖżļĪ£ņØś ļ¦ÉņØ┤ļéś ĻĖĆ, Ē¢ēļÅÖ ļō▒ņØä ņ¦æņżæņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ĒĢśņŚ¼ ĒĢ┤ņäØĒĢśĻ│Ā ņØśļ»Ėļź╝ ņ░Šņ£╝ļĀżļŖö ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļ░®ļ▓Ģ ņØ┤ļŗż. ņ¦łņĀü ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļ░®ļ▓ĢņØĆ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļīĆņāüņ×ÉņØś Ļ┤ĆņĀÉņŚÉņä£ ņäĖņāüĻ│╝ ņé¼ļ¼╝ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņØ┤ĒĢ┤Ļ░Ć ņżæņŗ¼ņØ┤ ļÉśĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņŚÉ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ ļīĆņāüņØ┤ ņäĖņāüĻ│╝ ņé¼ļ¼╝ņØä ņ¢┤ļ¢╗Ļ▓ī ļ│┤ļŖöņ¦ĆņŚÉ ļö░ļźĖ ļīĆņāüņ×ÉņØś Ē¢ēņ£äņÖĆ Ē¢ēņ£äņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢ ļ░®ņŗØņØä ļō£ļ¤¼ļé┤ņżĆļŗż(Creswell, 2007/2010/2013). ĻĘĖļלņä£ ņØ┤ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļŖö ņ¦łņĀü ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņØś ņäżļ¼Ėņ¦Ćļ▓ĢĻ│╝ ņé¼ļĪĆ ļČäņäØ ļ░®ļ▓ĢņØä ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢļōżņØä Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖņĀü Ļ┤ĆņĀÉņ£╝ļĪ£ ļČäņäØĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņØ┤ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļŖö ļśÉĒĢ£, ņäżļ¼Ė Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ņÖĆ ņä£ņłĀņØæļŗĄļōżņØäĒ¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖņØ┤ļĪĀļōżņØ┤ ņ¢┤ļŖÉņĀĢļÅäņäż ļ¬ģĒĢśļŖöĻ░Ćļź╝ļČäņäØĒĢśĻ│ĀĒÅēĻ░ĆĒĢśĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņŚÉ ĻĘĆļé®ņĀü ņĀæĻĘ╝ļ▓ĢņØ┤ ņĀüņÜ®ļÉśņŚłļŗż.
ņé¼ļĪĆļČäņäØņØĆ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ĒĢśĻ│Āņ×É ĒĢśļŖö ņŻ╝ņĀ£ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢśņŚ¼ Ļ╣ŖĻ│Ā ņāüņäĖĒĢ£ Ļ│Āņ░░, ļČäņäØĻ│╝ Ļ▓ĆĒåĀļź╝ ĒĢśļŖö ņ¦łņĀü ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņØś ĒĢ£ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ ļ░®ļ▓ĢņØ┤ļ®░, ņØ┤ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ ļ░®ļ▓ĢņØĆņŗżņāØĒÖ£ņŚÉņä£ ņØ╝ņ¢┤ļéśļŖö ĒśäņāüļōżņØä ļ¼śņé¼, ĒāÉņāē ļśÉļŖö ņäżļ¬ģĒĢśļŖöļŹ░ ņĀüĒĢ®ĒĢ£ ļ░®ļ▓ĢļĪĀņØ┤ļŗż. ņé¼ļĪĆļČäņäØņØĆ ļśÉĒĢ£, ļŗ©ņł£ĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņØĆ ņāüĒÖ®, Ē¢ēĒā£ņÖĆ ļ¼ĖĒÖöņĀü ņÜöņåīļōżņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņØ┤ĒĢ┤ļź╝ ļåÆņØ┤ļŖöļŹ░ ņĀüĒĢ®ĒĢ£ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļ░®ļ▓ĢņØ┤ĻĖ░ļÅä ĒĢśļŗż (Stake, 1995; Yin, 2014). ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļ░®ļ▓ĢņØś ĒĢśļéśļĪ£ņŹ©, ņé¼ļĪĆļČäņäØņØĆ ņé¼ĒÜīĻ│╝ĒĢÖĻ│╝ ņāØļ¬ģĻ│╝ĒĢÖļČäņĢ╝ņŚÉņä£ ļäÉļ”¼ ņØ┤ņÜ®ļÉśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż (Yin, 2009).
Ļ▓ĮņśüĒĢÖņŚÉņä£ ņé¼ļĪĆļČäņäØņØĆ ņÖĖļČĆņĀü ņśüĒ¢źĻ│╝ ĻĘĖ ņśüĒ¢źņØ┤ ĻĖ░ņŚģņŚÉ ļ»Ėņ╣śļŖö ļé┤ņÜ®ļōżņØä ļČäņäØĒĢśĻ▒░ļéś, ĻĖ░ņŚģņØś ņĀäļץ, ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢ ļśÉļŖö ņØ┤ĒĢ┤Ļ┤ĆĻ│äļź╝ ņØ┤ĒĢ┤ĒĢśĻ▒░ļéś, ņĄ£ņĀüņØś Ļ▓Įņśüņé¼ļĪĆļōżņØä Ļ░£ļ░£ĒĢśļŖöļŹ░ ņŻ╝ļĪ£ ņØ┤ņÜ®ļÉśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż(Klonoski, 2013). ļ│Ė ļģ╝ļ¼ĖņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņäżļ¼ĖņĪ░ņé¼ņÖĆ ļŹöļČłņ¢┤ ņé¼ļĪĆ ļČäņäØņØä ņ¦äĒ¢ēĒĢśņŚ¼ ļģ╝ļ¼ĖņØś ņĀĢĒÖĢņä▒Ļ│╝ ņŗĀļó░ņä▒ ĒÖĢļ│┤ņŚÉ ļģĖļĀźĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņé¼ļĪĆņØś ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢ ļŗ╣ņŗ£ ņāüĒÖ®ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņä£ņłĀ ņØæļŗĄļōżņØĆ ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£ĄĒöäļĪ£ņĀØĒŖĖļź╝ņ¦äĒ¢ēĒĢ£ņŗżņĀ£ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņé¼ņØśņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ąļŗ┤ļŗ╣ņ×ÉļōżņŚÉĻ▓īņä£ ĒÖĢļ│┤ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ĒÖĢļ│┤ĒĢ£ņä£ņłĀņØæļŗĄņØäĒåĄĒĢśņŚ¼, ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£ĄņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢļŗ╣ņŗ£ņØś ļé┤ ┬ĘņÖĖļČĆņØśņāüĒÖ®Ļ│╝ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢ ļ░░Ļ▓ĮņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņĀĢļ│┤ļōżņØä ļČäņäØĒĢśņŚ¼ ļģ╝ļ¼ĖņØś ņŗĀļó░ņä▒ Ē¢źņāüņŚÉ ļģĖļĀźĒĢśņśĆĻ│Ā, ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢ Ēøä ļ░£ņāØĒĢ£ ĒśäņāüĻ│╝ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ņāüņäĖĒ׳ļČäņäØĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņä£ņłĀņØæļŗĄņŚÉņ░ĖņŚ¼ĒĢ┤ņżĆņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ąņŗżļ¼┤ņ×ÉļōżņØĆ ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ĻĖ░ņŚģņØś ņĄ£ņóģ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņ×ÉĻ░Ć ņĢäļŗłļ»ĆļĪ£, ļ╣äĒĢ®ļ”¼ņĀüņØ┤Ļ▒░ļéś ņåÉņŗżņØ┤ ļ░£ņāØļÉ£ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņ▒ģņ×äņ£╝ļĪ£ļČĆĒä░ ļ╣äĻĄÉņĀü ņ×Éņ£ĀļĪ£ņÜ┤ ņ×ģņןņØ┤ļŗż.
ņä£ņłĀ ņØæļŗĄņ×ÉļōżņØĆ 2010ļģä ļŗ╣ņŗ£ AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņŚÉņä£ ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņŚģļ¼┤ļź╝ ļ¦ĪņĢśļŹś ņ×äņ¦üņøÉ 3ļ¬ģņØ┤ļ®░, ņä£ņłĀņØæļŗĄņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņ¦łļ¼ĖņØś ļé┤ņÜ®ņØĆ ņĢäļלņÖĆ Ļ░Öļŗż.
2010ļģä ņ║ĀņĮöņÖĆ Supramax ļ▓īĒü¼ņäĀ 6ņ▓Ö ņŗĀņĪ░ ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņŚģļ¼┤ ņ¦äĒ¢ēņŗ£, ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤Ļ▓ĮĻĖ░ĒĢśļØĮĻ│╝ ņ¦ĆņåŹņĀüņØĖ ņäĀĻ░Ć ĒĢśļØĮļĢīļ¼ĖņŚÉ ņ║ĀņĮöņŚÉņä£ļŖö ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņŗĀņĪ░ņäĀļ░ĢņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ĒÖĢļ│┤ļ│┤ļŗżļŖö ņäĀļ░ĢņØĖļÅä ĒżĻĖ░ļź╝ ņĀ£ņĢł Ē¢łņŚłņŖĄļŗłļŗż. ĻĘĖļŗ╣ņŗ£ ņäĀĻ░Ć ĒĢśļØĮņČöņäĖņŚÉļÅä ļČłĻĄ¼ĒĢśĻ│Ā, ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņĪ░ļŗ¼ņØä ĒåĄĒĢ£ ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņäĀļ░ĢņØĖļÅäļź╝ ņäĀĒāØĒĢśņŗĀ ļé┤ļČĆņØś ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢ ļ░░Ļ▓ĮĻ│╝ ļīĆļé┤ņÖĖ ņŗ£ņן ņāüĒÖ®ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņ×ÉņäĖĒĢ£ ņäżļ¬ģņØä ļČĆĒāü ļō£ļ”Įļŗłļŗż.
ņäżļ¼Ėņ¦ĆļŖö ņĪ░ņé¼ļ¬®ņĀüņŚÉ ļ¦×ļŖö ņ£ĀņÜ®ĒĢ£ ņ×ÉļŻīļź╝ ņłśņ¦æĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢśņŚ¼ Ļ░Ćņן ļ¦ÄņØ┤ ņé¼ņÜ®ļÉśļŖö ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņĀüņØĖ ņłśļŗ©ņØ┤ļŗż. ņäżļ¼Ėņ¦Ćļ▓ĢņØĆ ņØæļŗĄņ×ÉņØś ļŗĄļ│ĆņØä ņÜöĒĢśļŖö ņØ╝ļĀ©ņØś ņ¦łļ¼ĖļōżļĪ£ ĻĄ¼ņä▒ļÉ£ ņäżļ¼Ėņ¦Ćļź╝ ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņĪ░ņé¼ĒĢśļŖö ļ░®ļ▓Ģņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ░Ćņן ļīĆĒæ£ņĀüņØĖ 1ņ░© ņ×ÉļŻī ņłśņ¦æļ░®ļ▓ĢņØ┤ļŗż. ļśÉĒĢ£ ļŗżņ¢æĒĢ£ ļ░®ļ▓Ģņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ¦łļ¼ĖņØä ĻĄ¼ņä▒ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņŚÉ ņäżļ¼Ėņ¦Ćļ▓ĢņØĆ ņ£ĄĒåĄņä▒Ļ│╝ Ļ░ØĻ┤Ćņä▒ņØ┤ ļåÆņØĆ ņ×ÉļŻīņłśņ¦æļ░®ļ▓ĢņØ┤ļŗż. (Lee, 2010)
ņäżļ¼ĖĻ│╝Ļ┤ĆļĀ©ļÉ£ņ¦łļ¼ĖĻ│╝ņäĀĒāØļŗĄņĢłņØśņ£ĀĒśĢļōżņØĆļ¼ĖĒŚīņĪ░ņé¼ļź╝ļ░öĒāĢņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ×æņä▒ļÉśņŚłļŗż. Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖņ×ÉļōżņØ┤ Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖ ņØ┤ļĪĀļōżņØä ņ×ģņ”ØĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ņä£ ņŗżĒ¢ēĒĢ£ ņäżļ¼ĖņĪ░ņé¼ ņ£ĀĒśĢļōżĻ│╝ ļ¼ĖņןļōżņØä ņ░ĖņĪ░ĒĢśņŚ¼, ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņäżļ¼ĖĻ│╝ ļŗĄļ│ĆņØä ņżĆļ╣äĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņ¦łļ¼ĖĻ│╝ ņäĀĒāØ ļŗĄļ│ĆļōżņØĆ ņŗżņĀ£ Ļ│╝Ļ▒░ņŚÉ KAMCOĻ░Ć ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ĻĖ░ņŚģļōżĻ│╝ ņ¦äĒ¢ēĒĢśņśĆļŹś ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ĒöäļĪ£ņĀØĒŖĖļōżņØś ĒśæņāüņØä ĻĖ░ļ░śņ£╝ļĪ£ ņżĆļ╣äĒĢśņśĆļŗż.
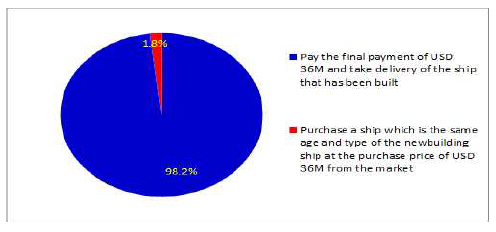
ĒÜīņé¼ņØś ņäĀļīĆ ĒÖĢļ│┤Ļ│äĒÜŹņŚÉ ļö░ļØ╝, ļŗ┤ļŗ╣ņ×ÉļŖö ņĪ░ņäĀņåīņŚÉ 2ļģäņĀä Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ Ļ░ĆĻ▓® USD 40MņŚÉ ņäĀļ░ĢĻ▒┤ņĪ░Ļ│äņĢĮņØä ņ▓┤Ļ▓░ĒĢśĻ│Ā, Ļ│äņĢĮĻĖłņ£╝ļĪ£ USD 4Mļź╝ ņ¦ĆĻĖēĒĢśņśĆņŖĄļŗłļŗż. ņ×öĻĖł USD 36MņØä ņ¦ĆĻĖēĒĢ┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢśļŖö Ēśäņ×¼, ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ņäĀļ░ĢņØś ņŗ£ņןĻ░ĆĻ▓®ņØĆ USD 36Mņ×ģļŗłļŗż. ņäĀļ░ĢņØĖļÅäņÖĆ ņ×öĻĖłņ¦ĆĻĖēņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļ│ĖņØĖņØś ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢ ĒīÉļŗ©ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņØśĻ▓¼ņØä ļČĆĒāü ļō£ļ”Įļŗłļŗż. ļŗ©, ņäĀļ░ĢņØĖļÅä ĒżĻĖ░ņŗ£ Ļ│äņĢĮĻĖł ņÖĖ ļ│äļÅäņØś ņČöĻ░ĆņĀü ņ£äņĢĮĻĖł ļō▒ņØĆ ņĪ┤ņ×¼ĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖļŖöļŗżļŖö Ļ░ĆņĀĢņ×ģļŗłļŗż.
- ņ×öĻĖłņØä ņ¦ĆĻĖēĒĢśĻ│Ā, Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņäĀļ░ĢņØä ņØĖļÅäļ░øļŖöļŗż.
- Ļ│äņĢĮĻĖłĻ│╝ ņäĀļ░ĢņØĖļÅäļź╝ ĒżĻĖ░ĒĢśĻ│Ā, ņŗ£ņןņŚÉņä£ ļÅÖņØ╝ ņäĀļĀ╣, ļÅÖĒśĢ ņäĀļ░ĢņØä USD 36MņŚÉ ĻĄ¼ņ×ģĒĢ£ļŗż.
ĒÜīņé¼ņØś ņäĀļīĆ ĒÖĢļ│┤Ļ│äĒÜŹņŚÉ ļö░ļØ╝, ļŗ┤ļŗ╣ņ×ÉļŖö ņĪ░ņäĀņåīņŚÉ 2ļģäņĀä Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ Ļ░ĆĻ▓® USD 40MņŚÉ ņäĀļ░ĢĻ▒┤ņĪ░Ļ│äņĢĮņØä ņ▓┤Ļ▓░ĒĢśĻ│Ā, Ļ│äņĢĮĻĖłņ£╝ļĪ£ USD 4Mļź╝ ņ¦ĆĻĖēĒĢśņśĆņŖĄļŗłļŗż. ņ×öĻĖł USD 36MņØä ņ¦ĆĻĖēĒĢ┤ņĢ╝ĒĢśļŖö Ēśäņ×¼, ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ņäĀļ░ĢņØś ņŗ£ņןĻ░ĆĻ▓®ņØĆ USD 34Mņ×ģļŗłļŗż. ņäĀļ░ĢņØĖļÅäņÖĆ ņ×öĻĖłņ¦ĆĻĖēņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļ│ĖņØĖņØś ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢ ĒīÉļŗ©ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņØśĻ▓¼ņØä ļČĆĒāüļō£ ļ”Įļŗłļŗż. ļŗ©, ņäĀļ░ĢņØĖļÅä ĒżĻĖ░ņŗ£ Ļ│äņĢĮĻĖłņÖĖ ļ│äļÅäņØś ņČöĻ░ĆņĀü ņ£äņĢĮĻĖł ļō▒ņØĆ ņĪ┤ņ×¼ĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖļŖöļŗżļŖö Ļ░ĆņĀĢņ×ģļŗłļŗż.
- ņ×öĻĖłņØä ņ¦ĆĻĖēĒĢśĻ│Ā, Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņäĀļ░ĢņØä ņØĖļÅäļ░øļŖöļŗż.
- Ļ│äņĢĮĻĖłĻ│╝ ņäĀļ░ĢņØĖļÅäļź╝ ĒżĻĖ░ĒĢśĻ│Ā, ņŗ£ņןņŚÉņä£ ļÅÖņØ╝ ņäĀļĀ╣, ļÅÖĒśĢ ņäĀļ░ĢņØä USD 34MņŚÉ ĻĄ¼ņ×ģĒĢ£ļŗż
ĒÜīņé¼ņØś ņäĀļīĆ ĒÖĢļ│┤Ļ│äĒÜŹņŚÉ ļö░ļØ╝, ļŗ┤ļŗ╣ņ×ÉļŖö ņĪ░ņäĀņåīņŚÉ 2ļģäņĀä Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ Ļ░ĆĻ▓® USD 40MņŚÉ ņäĀļ░ĢĻ▒┤ņĪ░Ļ│äņĢĮņØä ņ▓┤Ļ▓░ĒĢśĻ│Ā, Ļ│äņĢĮĻĖłņ£╝ļĪ£ USD 4Mļź╝ ņ¦ĆĻĖēĒĢśņśĆņŖĄļŗłļŗż. ņ×öĻĖł USD 36MņØä ņ¦ĆĻĖēĒĢ┤ņĢ╝ĒĢśļŖö Ēśäņ×¼, ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ņäĀļ░ĢņØś ņŗ£ņןĻ░ĆĻ▓®ņØĆ USD 32Mņ×ģļŗłļŗż. ņäĀļ░ĢņØĖļÅäņÖĆ ņ×öĻĖłņ¦ĆĻĖēņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļ│ĖņØĖņØś ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢ ĒīÉļŗ©ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņØśĻ▓¼ņØä ļČĆĒāüļō£ ļ”Įļŗłļŗż. ļŗ©, ņäĀļ░ĢņØĖļÅä ĒżĻĖ░ņŗ£ Ļ│äņĢĮĻĖłņÖĖ ļ│äļÅäņØś ņČöĻ░ĆņĀü ņ£äņĢĮĻĖł ļō▒ņØĆ ņĪ┤ņ×¼ĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖļŖöļŗżļŖö Ļ░ĆņĀĢņ×ģļŗłļŗż.
- ņ×öĻĖłņØä ņ¦ĆĻĖēĒĢśĻ│Ā, Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņäĀļ░ĢņØä ņØĖļÅäļ░øļŖöļŗż.
- Ļ│äņĢĮĻĖłĻ│╝ ņäĀļ░ĢņØĖļÅäļź╝ ĒżĻĖ░ĒĢśĻ│Ā, ņŗ£ņןņŚÉņä£ ļÅÖņØ╝ ņäĀļĀ╣, ļÅÖĒśĢ ņäĀļ░ĢņØä USD 32MņŚÉ ĻĄ¼ņ×ģĒĢ£ļŗż
ņäżļ¼Ė ņ░ĖņŚ¼ņ×ÉļŖö ļīĆļČĆļČä ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤Ļ│╝ ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£ĄņŚģĻ│ä ņóģņé¼ņ×ÉļĪ£ ņśżļ×£ ĻĖ░Ļ░ä ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£ĄĻ┤ĆļĀ© ņŚģļ¼┤ļź╝ ņ¦ü┬ĘĻ░äņĀæņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ¦äĒ¢ēĒ¢łļŹś ņŚģĻ│äņØś ņŗżļ¼┤ņ×É Ļ▓Ė ņĀäļ¼ĖĻ░ĆļōżņØ┤ļŗż. ņäżļ¼Ė ņ░ĖņŚ¼ņ×Éņżæ ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ ĻĖ░ņŚģ ņóģņé¼ņ×ÉļŖö 14ļ¬ģņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĀäņ▓┤ ņżæ 24.6%ļź╝ ņ░©ņ¦ĆĒ¢łļŗż. ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£ĄĻ┤ĆļĀ© ĻĖ░Ļ┤ĆņØś ņóģņé¼ņ×ÉļŖö 36.8%, ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ ņżæĻ░£ņŚģ ņóģņé¼ņ×ÉļŖö 12.3%, ĻĖ░ĒāĆ ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ ņ£ĀĻ┤Ć ĻĖ░Ļ┤ĆņØĆ 14%, ĻĖ░ĒāĆ ĻĖ░Ļ┤Ć ņóģņé¼ņ×ÉļŖö 12.3%ņśĆļŗż. ņäżļ¼Ė ņ░ĖņŚ¼ņ×ÉļōżņØś ņŚģļ¼┤ Ļ▓ĮļĀźņØĆ 5ļģä ņØ┤ĒĢśĻ░Ć 5.3%, 10ļģä ņØ┤ĒĢśĻ░Ć 10.5%, 15ļģä ņØ┤ĒĢśĻ░Ć 38.6%, 20ļģä ņØ┤ĒĢśĻ░Ć 24.6%, 30ļģäņØ┤ĒĢśĻ░Ć 14%, 30ļģäņØ┤ņāüņØ┤ 7%ļĪ£ ļīĆļČĆļČä ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤Ļ│╝ ņäĀļ░Ģ ĻĖłņ£ĄĻ┤ĆļĀ© ņĀäļ¼ĖĻ░ĆļōżņØ┤ņŚłļŗż. ņäżļ¼Ė ņ░ĖņŚ¼ņ×ÉļōżņØś ņŚ░ļĀ╣ļīĆļŖö 30ļīĆ ņØ┤ņāü 28.1%, 40ļīĆ ņØ┤ņāü 54.4%, 50ļīĆ ņØ┤ņāü 10.5%, 60ļīĆņØ┤ņāü 7%ļĪ£ ļīĆļČĆļČä ņŚ░ļź£ņØ┤ ņ׳ļŖö ņĀäļ¼ĖĻ░Ć ļČäļōżņØ┤ ņäżļ¼ĖņŚÉ ņ░ĖņŚ¼ĒĢśņśĆļŗż.
2007ļģäņŚÉ AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņØĆ ĒÖŹņĮ® ņäĀņŻ╝Ļ░Ć ņżæĻĄŁņĪ░ņäĀņåīņŚÉ Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ ļ░£ņŻ╝ĒĢ£ 6ņ▓ÖņØś Supramax Ļ▒┤ņĪ░Ļ│äņĢĮņØä ņ▓Öļŗ╣USD 44.5MņŚÉ ļ¦żņ×ģĒ¢łĻ│Ā, Ļ│äņĢĮĻĖłņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ▓Öļŗ╣ USD 6.675MņØä ņ¦ĆĻĖēĒ¢łļŗż (Ang, 2007; Clarkson Research Services, 2007; Kwak, 2010). 2010ļģä ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņäĀļ░ĢņØś ņŗ£ņןĻ░ĆĻ▓®ņØĆ ņ▓Öļŗ╣ USD 34MņØ┤ņŚłņ£╝ļ®░, Ļ░ĆĻ▓®ņØĆ Ļ│äņåŹ ĒĢśļØĮĒĢśļŖö ņČöņäĖņśĆļŗż. ņØ┤ ņŗ£ņĀÉņŚÉ AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņØĆ KAMCOņŚÉ ņØĖļÅä ļīĆĻĖłĻ│╝ Ļ┤ĆļĀ©ļÉ£ ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņ¦ĆņøÉņØä ņÜöņ▓ŁĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņ▓Öļŗ╣ ņØĖļÅä ļīĆĻĖłņØĆ USD 37.825M ņØ┤ņŚłņ£╝ļ®░, ļŗ╣ņŗ£ ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņäĀļ░ĢņØś ņŗ£ņן Ļ░ĆĻ▓®ņØĆ ņ▓Öļŗ╣ USD 34MņØ┤ņŚłļŗż. KAMCOļŖö ļ░ĆļĀżņ׳ļŖö ņŗĀņĪ░ ņäĀļ│Ąļ¤ēĻ│╝ ĒĢśļØĮņäĖņØĖ ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ ņŗ£ĒÖ® ļō▒ņØä Ļ│ĀļĀżĒĢśņŚ¼, ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņé¼ņŚÉ ņäĀļ░Ģ ņØĖļÅä ĒżĻĖ░ļź╝ ĻČīĻ│ĀĒĢśņśĆņ£╝ļéś, ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņé¼ļŖö ĻĖ░ļé®ļČĆļÉ£Ļ│äņĢĮĻĖłļō▒ņØäņØ┤ņ£ĀļĪ£ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ąņ¦ĆņøÉņØäņÜöņ▓ŁĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ņŗ£ņĀÉņØĆ Ļ│äņĢĮņä£ņŚÉ ļ¬ģņŗ£ļÉ£ ņäĀļ░Ģ ņØĖļÅä ļé®ĻĖ░ņØ╝ņØä ņ¦Ćļé£ ņŗ£ņĀÉņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ│äņĢĮ ĒīīĻĖ░ņŚÉ Ēü░ ļ¼ĖņĀ£Ļ░Ć ņŚåļŖö ņāüĒÖ®ņØ┤ņŚłņØīņŚÉļÅä ļČłĻĄ¼ĒĢśĻ│Ā, AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņØĆ ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£ĄņØä ņ¦ĆņøÉļ░øņĢä ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņäĀļ░ĢļōżņØä ņĪ░ņäĀņåīļĪ£ļČĆĒä░ ņØĖļÅä ļ░øņĢśļŗż.
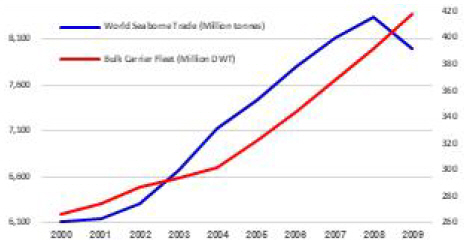
ļ¦łĒŗ┤ ņŖżĒå▒Ēżļō£ ĻĄÉņłśĻ░Ć ņō┤ Maritime Economics 3ĒÄĖņØä ļ│┤ļ®┤, ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņŗ£ņןņŚÉņä£ ņŗ£ĒÖ®ņŚÉ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ņŻ╝ļŖö ņłśņÜö ņĖĪļ®┤ ņÜöņåīļōżņØĆ ĻĄŁņĀ£ Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ ņāüĒÖ®, ĒĢ┤ņāüļ¼╝ļÅÖļ¤ē, Ēåż-ļ¦łņØ╝, ļīĆĒśĢ ņØ┤ļ▓żĒŖĖ ļō▒ņØ┤Ļ│Ā Ļ│ĄĻĖē ņĖĪļ®┤ņØś ņÜöņåīļōżņØĆ ņĀäņäĖĻ│ä ņäĀļ│Ąļ¤ē, ņäĀļ░ĢņØś ņāØņé░ņä▒, ņĪ░ņäĀņåī ņāØņé░ņä▒, ņŖżĒü¼ļ×® ļō▒ņØ┤ļØ╝Ļ│Ā ļ¬ģņŗ£ļÉśņ¢┤ņ׳ļŗż. ņØ┤ Ļ░ÖņØĆ ļé┤ņÜ®ļōżņØĆ ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņŚģĻ│ä ņóģņé¼ņ×Éļōż ņŚÉĻ▓ī ņØ╝ļ░śņĀü ņāüņŗØņØ┤ļŗż(Stopford, 2009). ļśÉĒĢ£, ņŖżĒå▒Ēżļō£ ĻĄÉņłśļŖö ņ▒ģņŚÉņä£ Ļ│╝Ļ▒░ ņłśņ╣śņÖĆ ļŹ░ņØ┤Ēä░ļź╝ ļ│┤ļ®┤ ļ¬ģĒÖĢĒĢśĻ▓ī ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņØĆ Ļ▓ĮĻĖ░ ņé¼ņØ┤Ēü┤ņØ┤ ņĪ┤ņ×¼ĒĢśļŖö ņé░ņŚģņØ┤Ļ│Ā, ļ”¼ļ©╝ ņé¼Ēā£ņØ┤Ēøä ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņŗ£ņןņØĆ ņןĻĖ░ ļČłĒÖ®ņØ┤ ņśłĻ▓¼ļÉ£ļŗżĻ│Ā ļ░ØĒśöļŗż. ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ ņĀäļ¼ĖĻ░ĆļōżņØĆ 2000ļģäļīĆ Ēøäļ░śņŚÉ ļōżņ¢┤ņä£ļ®┤ņä£, 2000ļģäļīĆ ņżæļ░ś ņŚŁņé¼ņāü ņ£ĀļלņŚåļŖö ņ┤łĒśĖĒÖ®ĻĖ░ļź╝ Ļ▓¬ņŚłļŹś ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ ņŗ£ņןņØä ļ╣äĻ┤ĆņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ│┤Ļ│Ā ņ׳ņŚłļŗż. ŌĆ£The higher the mountain, the deeper its ridgesŌĆØ ĻĄ¼ņĀłņØä ņØĖņÜ®ĒĢśļ®░, ņןĻĖ░Ļ░ä ļČłĒÖ®ņØ┤ ņśłņāüļÉ£ļŗżĻ│Ā Ļ░üņóģ ļ│┤Ļ│Āņä£ļź╝ ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ņŻ╝ņןĒ¢łļŗż (Sand, 2010; Stopford, 2009(2)).
ņāüĻĖ░ ĻĘĖļלĒöäņÖĆ ĒģīņØ┤ļĖöņŚÉņä£ ļ│┤ļō»ņØ┤, ļ▓īĒü¼ņäĀņØś ņ▓ÖņłśņÖĆ ņäĀļ│Ąļ¤ēņØĆ 2009ļģäĻ╣īņ¦Ć ļ╣Āļź┤Ļ▓ī ņ”ØĻ░ĆļÉśņŚłļŗż. 2009ļģäņŚÉļŖö ņĀä ņäĖĻ│ä ĒĢ┤ņāü ļ¼╝ļÅÖļ¤ē ņ”ØĻ░Ć ņČöņäĖņŚÉ ņĀ£ļÅÖņØ┤ Ļ▒Ėļ”¼Ļ│Ā ĒĢ┤ņāü ļ¼╝ļÅÖļ¤ēņØ┤ ņĀäļģäļÅä ļ│┤ļŗż ņżäņŚłņ£╝ļéś, ļ▓īĒü¼ņäĀ ņäĀļ│Ąļ¤ē ņ”ØĻ░ĆņäĖļŖö Ļ│äņåŹ Ļ░ĆĒīīļź┤Ļ▓ī ļŖśņ¢┤Ļ░öļŗż. ĒĢśĻĖ░ ĻĘĖļלĒöäļŖö ņżæĻĄŁņĪ░ņäĀņåīļōżņŚÉ2009ļģäĻ╣īņ¦Ćļ░£ņŻ╝ļÉ£ņŗĀņĪ░ļ░£ņŻ╝ļ¤ēņØäļéśĒāĆļéĖĻĘĖļלĒöäņØ┤ļŗż. ņżæĻĄŁ ņĀĢļČĆļŖö ņżæĻĄŁļé┤ ņŗżņŚģļ¼ĖņĀ£ņÖĆ ņé¼ĒÜīņØ┤ņŖłļōżņØä ĒĢ┤Ļ▓░ĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ņä£ ļīĆĻĘ£ļ¬©ļĪ£ ņĪ░ņäĀņåīļź╝ Ļ▒┤ņäżĒĢśņśĆļŗż (Ludwig and Tholen, 2006). ņØ┤ ņØśļ»ĖļŖö 2010ļģäļČĆĒä░ ļ¦ēļīĆĒĢ£ ņäĀļ│Ąļ¤ēņØ┤ ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņŗ£ņןņ£╝ļĪ£ ņŤņĢäņĀĖ ļōżņ¢┤ņś¼ ņśłņĀĢņØ┤ļŗżļØ╝ļŖö ļ£╗ņØ┤ņŚłļŗż.
2010ļģä AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņé¼Ļ░Ć KAMCOņŚÉ ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£ĄņØä ņØśļó░ĒĢĀ ļŗ╣ņŗ£ Ļ│╝Ļ▒░ ļŹ░ņØ┤Ēä░ļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢ┤ļ│Ė Ļ▓░Ļ│╝, AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņé¼Ļ░Ć 2007ļģäņŚÉ ņŗĀņĪ░ ļ░£ņŻ╝ĒĢśņŚ¼ Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņżæņØĖ Supramax ņäĀļ░ĢņØä ņ▓Öļŗ╣ USD 44.5MņŚÉ ĻĄ¼ļ¦żĒĢ£ Ļ▓░ņĀĢ ņØĆ Ēśäļ¬ģĒĢ£ Ēł¼ņ×ÉĻ▓░ņĀĢņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ│┤ĻĖ░ ņ¢┤ļĀżņøĀļŗż.
2007ļģäņŚÉ ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņäĀļ░ĢņØś ņżæĻ│ĀņäĀĻ░ĆņÖĆ ņŗĀņĪ░ņäĀĻ░ĆĻ░Ć ņŚŁņé¼ņāü ņĄ£Ļ│Āņ╣śļź╝ ĻĖ░ļĪØĒĢśļŹś ņŗ£ĻĖ░ņśĆļŗż. ņ¦ĆņåŹņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņŗ£ņןņŚÉ Ļ│ĄĻĖēļÉĀ ņŗĀņĪ░ ņäĀļ│Ąļ¤ēņØä Ļ│ĀļĀżĒĢĀ Ļ▓ĮņÜ░, ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņé¼ļŖö 2010ļģä ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņäĀļ░ĢņØä ņØĖļÅä ļ░øĻĖ░ļ│┤ļŗżļŖö Ļ│äņĢĮņØäĒżĻĖ░Ē¢łņ¢┤ņĢ╝Ē¢łļŗż. Ēü┤ļØĮņŖ©ņØ┤ņĀĢĻĖ░ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ņĀ£Ļ│ĄĒĢśļŖö2010ļģäņāüļ░śĻĖ░ ņŗ£ņןļ│┤Ļ│Āņä£ņŚÉņä£ļÅä ļīĆĻĘ£ļ¬© ņŗĀņĪ░ ņäĀļ░Ģ ņØĖļÅä ļ¼╝ļ¤ē ļĢīļ¼ĖņŚÉ Supramax ņÜ┤ņ×ä ņŗ£ņןņØĆ ņ¦ĆņåŹņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ¢┤ļĀżņøĆņŚÉ ņ¦üļ®┤ĒĢĀ Ļ▓āņØ┤ļØ╝Ļ│Ā ņśłņĖĪĒ¢łļŗż.
AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņé¼Ļ░Ć 2007ļģä ĻĖ░ Ļ│äņĢĮļÉ£ ņŗĀņĪ░ Ļ│äņĢĮņØä ņ▓Öļŗ╣ USD 44.5MļĪ£ ĻĄ¼ņ×ģĒĢĀ ļŗ╣ņŗ£, Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ Ēøä 5ļģäļÉ£ Supramax ņäĀļ░ĢņØś ņŗżņĀ£ Ļ▒░ļל ņżæĻ│Ā ņäĀĻ░ĆļŖö USD 75MņØ┤ņŚłļŗż. 2007ļģä AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņé¼ņØś Ļ▓Įņśüņ¦äņØĆ ņżæĻ│Ā ņäĀĻ░ĆņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦ü ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļĪ£ ļ¦żņ×ģņØä Ļ│ĀļĀżĒ¢łļŹś ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņŗĀņĪ░ Ļ│äņĢĮņØś Ē¢źĒøä Ļ░Ćņ╣śĻ░Ć ņĄ£ņåīĒĢ£ USD 44.5Mļ│┤ļŗżļŖö ļåÆņØä Ļ▓āņØ┤ļØ╝Ļ│Ā ĒīÉļŗ©ĒĢśĻ│Ā ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ Ļ│äņĢĮņØä ļ¦żņ×ģĒ¢łļŹś Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ņČöļĪĀļÉ£ļŗż.
ņä£ņłĀņØæļŗĄņ×É A2ņÖĆ A3Ļ░Ć ņĀ£Ļ│ĄĒĢ£ ņä£ņłĀ ņØæļŗĄ ļé┤ņÜ®ņŚÉļÅä ņĀĢĒÖĢĒ׳ ņāüĻĖ░ ļé┤ņÜ®ņØ┤ ņ¢ĖĻĖēļÉśņ¢┤ņ׳ļŗż. ņä£ņłĀ ņØæļŗĄ ļé┤ņÜ®ņØä ļ│┤ļ®┤ ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņäĀļ░ĢņØ┤ Ļ│╝Ļ▒░ņŚÉ USD 70M ņØ┤ņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ▒░ļלļÉśņŚłļŹś ņäĀļ░ĢņØ┤ņŚłĻĖ░ņŚÉ ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņäĀļ░ĢļōżņØä ņØĖļÅä ļ░øĻĖ░ļĪ£ Ļ▓░ņĀĢĒ¢łļŗżĻ│Ā ļ¬ģņŗ£Ē¢łļŗż. Whyte and Sebenius(1997)ļŖöļČłĒÖĢņŗżĒĢ£ ņāüĒÖ®ņŚÉņä£ņé¼ļ×īļōżņØ┤ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØä ĒĢĀ Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ņ░ĖņĪ░ņĀÉņØś ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ░øļŖöļŗżĻ│Ā ņŻ╝ņןĒ¢łļŗż. Wright and Anderson(1989)ņØĆ ņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦ü ĒÜ©Ļ│╝Ļ░Ć ņé¼ļ×īļōżņØś ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņŚÉ ņ¦Ćļ░░ņĀüņØĖ ņŚŁĒĢĀņØä ĒĢ£ļŗżĻ│Ā ļ¬ģņŗ£Ē¢łļŗż. ņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦ü ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļŖö Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖņØ┤ļĪĀņżæĒĢśļéśļĪ£AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņØśņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£ĄņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņŚÉņśüĒ¢źņØäņŻ╝ņŚłļŗż.
AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņØĆ2010ļģäKAMCOņŚÉņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£ĄņØäņÜöņ▓ŁĒĢśĻĖ░ņĀäņŚÉĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņŗ£ņןņØä ļāēņ▓ĀĒ׳ļČäņäØĒ¢łņ¢┤ņĢ╝Ē¢łļŗż. ĻĘĖļ”¼Ļ│Ā, ĻĘĖļōżņØĆĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ņäĀĒśĢņØśĻ▓ĮņĀ£ņĀüĻ░Ćņ╣śĻ░Ć ļåÆņ¦Ć ņĢŖļŗżļ×Ć ņé¼ņŗżņØä ņØĖņ¦ĆĒ¢łņ¢┤ņĢ╝ Ē¢łļŗż. ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī, AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņØĆĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ņäĀļ░ĢļōżņØ┤ Ļ│äņĢĮņä£ņāü ļ¬ģņŗ£ļÉ£ņØĖļÅä ļé®ĻĖ░ņØ╝ņØäļäśĻ▓╝ņØīņŚÉļÅä ļČłĻĄ¼ĒĢśĻ│Ā Ļ│äņĢĮ ĒżĻĖ░ļź╝ ņäĀĒāØĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņĢśĻ│Ā, ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£ĄņØä ņ¦äĒ¢ēĒĢ┤ņä£ ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņäĀļ░ĢļōżņØä ņØĖļÅä ļ░øņĢśļŗż.
ļ¬©ļōĀ ņä£ņłĀ ņØæļŗĄņ×É A1, A2ņÖĆ A3ļŖö ņä£ņłĀņØæļŗĄņŚÉņä£ ņŗ£ņן ņäĀĻ░ĆĻ░Ć ļ░£ņŻ╝ĒĢ£ ņäĀļ░ĢņØś ņØĖļÅä ņ×öĻĖłļ│┤ļŗż ļé«ņĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī, ņØ┤ļ»Ė ņāüļŗ╣ĒĢ£ Ļ│äņĢĮĻĖłņØä ļé®ļČĆĒĢ£ ņāüĒā£ņśĆĻĖ░ņŚÉ ņäĀļ░Ģ ņØĖļÅäļź╝ ĒżĻĖ░ĒĢĀ ņłś ņŚåņŚłļŗżĻ│Ā ļ¬ģņŗ£Ē¢łļŗż. Ļ▒░ĻĖ░ņŚÉ ļŹöĒĢśņŚ¼, ļ¦īņĢĮ ņäĀļ░Ģ ņØĖļÅäļź╝ ĒżĻĖ░ĒĢśļ®┤, ĻĖ░ ļé®ļČĆĒĢ£ Ļ│äņĢĮĻĖłņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ┤ ņåÉņŗżņØä ņØĖņŗØĒĢ┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢśĻ│Ā ņØ┤ļŖö ņŗĀņĪ░ Ļ│äņĢĮ ĻĄ¼ļ¦żņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ Ļ▓Įņśüņāü ņŗżĒī©ļĪ£ ĒÅēĻ░ĆļÉśĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņŚÉ ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņäĀļ░ĢņØś ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņ¦æĒ¢ēņØä ņ¦äĒ¢ēĒĢ┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢ£ļŗżĻ│Ā ņĀüņŗ£Ē¢łļŗż. ĻĘĖļ”¼Ļ│Ā, AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņØś Ļ▓Įņśüņ¦äļōżņØĆ ņ¢ĖņĀĀĻ░Ć ņäĀĻ░ĆĻ░Ć ļŗżņŗ£ ĒÜīļ│ĄļÉśĻ│Ā, ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņäĀļ░ĢļōżņØ┤ ņłśņØĄņØä ņ░ĮņČ£ĒĢĀ Ļ▓āņØ┤ļØ╝ ņāØĻ░üĒ¢łļŗż.
Garland(1990)ļŖö ļ¦żļ¬░ļ╣äņÜ®ņØ┤ ņČöĻ░Ć Ēł¼ņ×É Ļ▓░ņĀĢņŚÉ ņ¦üņĀæņĀüņØĖ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ņżĆļŗżĻ│Ā ņŻ╝ņןĒ¢łļŗż. Arkes and Blumer(1985)ļŖö ņé¼ļ×īļōżņØ┤ Ēł¼ņ×É ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØ┤ ņלļ¬╗ļÉśņŚłņØīņØä ņØĖņ¦ĆĒĢ£ ĒøäņŚÉļÅä ļ¼┤ņŖ© ņØ┤ņ£ĀļĪ£ ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ĒöäļĪ£ņĀØĒŖĖņŚÉ Ļ│äņåŹ Ēł¼ņ×ÉĒĢśļŖöņ¦ĆņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ┤ ņäżļ¬ģņØä ĒĢśņśĆļŖöļŹ░, ĻĘĖ ņØ┤ņ£ĀļŖö Ēł¼ņ×Éļź╝ ņżæļŗ©ĒĢśļ®┤ ņåÉņŗżņØä ņØĖņĀĢĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤Ļ│Ā, ņ¦æĒ¢ēļÉ£ ņØśņé¼ Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØ┤ ņלļ¬╗ļÉ£ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØ┤ņŚłņØīņØä ņ×ÉņØĖĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņØ┤ļØ╝Ļ│Ā ņŻ╝ņןĒ¢łļŗż. Arkes and Ayton(1999)ņØĆ ņé¼ļ×īļōżņØ┤ ņŗżĒī©ĒĢ£ ĒöäļĪ£ņĀØĒŖĖņŚÉ ņ¦æņ░®ĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓ĮĒ¢źņØ┤ ņ׳ļŖöļŹ░, ĻĘĖ ņØ┤ņ£ĀļŖö ņØ┤ļ»Ė Ēł¼ņ×ģļÉ£ ņ×ÉņøÉļōżņØ┤ ļéŁļ╣äļĪ£ ĒÅēĻ░ĆļÉśļŖö Ļ▓āņØä ņøÉĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņØ┤ļØ╝Ļ│Ā ņŻ╝ņןĒ¢łļŗż.
AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņØĆ Supramax ņäĀļ░Ģ ĻĖłņ£ĄņØä ņ¦äĒ¢ēĒĢśļŖö ļÅÖņĢł, Ē¢ēļÅÖ ņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖ ņØ┤ļĪĀņŚÉļ¬ģņŗ£ļÉ£ļ¦żļ¬░ļ╣äņÜ®ņśżļźśņÖĆņŚźņ╣┤ĒÜ©Ļ│╝Ļ░ĆņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņŚÉņ¦Ćļ░░ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ņŻ╝ņŚłļŗż. ĻĖ░ ņ¦ĆĻĖēļÉ£ ņāüļŗ╣ĒĢ£ Ļ│äņĢĮĻĖłĻ│╝ Ļ▒┤ņĪ░Ļ│äņĢĮ ņäĀĻ░ĆĻ░Ć ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņŚÉ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ņżĆ Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ņä£ņłĀņØæļŗĄņŚÉ ļéśĒāĆļé¼ļŗż. ļ¦īņĢĮ AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņØś Ļ▓Įņśüņ¦äņØ┤ 2010ļģäņŚÉ KAMCOņØś ņĪ░ņ¢ĖļīĆļĪ£ ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņäĀļ░ĢļōżņØś ņØĖļÅäļź╝ ĒżĻĖ░Ē¢łļŗżļ®┤, AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņØĆ ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņäĀļ░ĢļōżļĪ£ ņØĖĒĢ£ ļ¦ē ļīĆĒĢ£ ņČöĻ░Ć ņåÉņŗż ļ░£ņāØņØä ļ¦ēņØä ņłś ņ׳ņŚłņØä Ļ▓āņØ┤ļŗż. ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ Supramax ņäĀļ░ĢļōżņØ┤ AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņØś ņśüņŚģ ņĀäļץņāü ĒĢäņÜöĒĢ£ ņäĀļ░ĢņØ┤ņŚłļŗżļ®┤, ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņé¼ļŖö ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņäĀĒśĢņØä ņŗ£ņןņŚÉņä£ ņÜ®ņäĀĒĢśņŚ¼ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśļŗżĻ░Ć 2011ļģä Ēś╣ņØĆ 2012ļģäņŚÉ USD 20M ņ┤łļ░śļīĆļĪ£ ņŗ£ņןņŚÉņä£ ļ¦żņ×ģĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ņŚłļŗż. ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī, ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņäĀļ░ĢļōżņØĆ AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņŚÉ Ļ╝Ł ĒĢäņÜöĒĢ£ ņĀäļץņĀü ĒĢäņłś ņäĀļ░ĢņØ┤ ņĢäļŗłņśĆļŗż. AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņØĆ ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņäĀļ░ĢņØś ņØĖļÅä ņŗ£ņĀÉĻ╣īņ¦Ć ņÜ®ņäĀņ▓śļź╝ ĻĄ¼ĒĢśņ¦Ć ļ¬╗ĒĢ┤ ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņäĀļ░Ģ ņØĖļÅä Ēøä Ļ▓©ņÜ░ Index ņŚ░ļÅÖ ņÜ┤ņ×äņ£╝ļĪ£ ļŗżļźĖ ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņé¼ņŚÉ ļīĆņäĀņØä ļé┤ļ│┤ļāłļŗż. KAMCOņØś Ļ░ĢĒĢ£ ņØĖļÅä ĒżĻĖ░ ĻČīĻ│ĀņŚÉļÅä ļČłĻĄ¼ĒĢśĻ│Ā, AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņØĆ ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņäĀļ░ĢņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņĪ░ļŗ¼ņØä ņŗżĒ¢ēĒ¢łĻ│Ā, ņŗ£ĒÖ® ĒĢśļØĮņŚÉ ļö░ļźĖ ņśüĒ¢źņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ¦ēļīĆĒĢ£ ņåÉņŗżņØä ņ×ģņŚłļŗż. AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņØś ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØĆ Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖņŚÉļ¬ģņŗ£ļÉ£ļ¦żļ¬░ļ╣äņÜ®ņśżļźśņÖĆņŚźņ╣┤ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļĪ£ļ¬ģņŠīĒ׳ņäżņĀĢļÉ£ļŗż.
ņÜ┤ņ×äņłśņ×ģĻ│╝ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ņäĀļ░ĢļōżņØśņØĖļÅäĻĖłņ£ĄņŚÉļīĆĒĢ£ņøÉĻ░Ćļź╝ļ╣äĻĄÉĒĢ┤ļ┤żņØäļĢī, Ļ░üņäĀļ░ĢļōżņØĆņāüĻĖ░ĻĘĖļלĒöäņ▓śļ¤╝ĻĖłņ£Ąļ¦īĻĖ░ņØĖ2014ļģäĻ╣īņ¦Ćļ¦ēļīĆĒĢ£ņåÉņŗżņØä ļ░£ņāØņŗ£ņ╝░ļŗż. AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņØĆ Supramax ņäĀļ░Ģ 5ņ▓ÖņØś ņØĖļÅä ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£ĄņØä KAMCOņÖĆ ņ¦äĒ¢ēĒĢśņśĆĻ│Ā, 2010ļģä 7ņøöļČĆĒä░ ņł£ņ░©ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØĖļÅäļÉ£ ņäĀļ░ĢļōżņØĆ ņ¦ĆņåŹņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņŚÉ ļ¦ēļīĆĒĢ£ ņåÉņŗżņØä ļ░£ņāØņŗ£ņ╝░ļŗż. ņāüĻĖ░ ĻĘĖļלĒöäņØś ļ╣©Ļ░ä ņäĀĻ│╝ ņāēņ£╝ļĪ£ Ēæ£ņŗ£ļÉ£ ļČĆļČäņØ┤ Break-even point ņØ┤Ļ│Ā Ēīīļ×ĆņāēņØ┤ ņŗżņĀ£ ņÜ┤ņ×ä ņłśņ×ģņØä ļéśĒāĆļéĖļŗż. SupramaxņäĀļ░ĢļōżņØś ņØĖļÅäļź╝ ĒżĻĖ░ĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖĻ│Ā, ņØĖļÅäļ░øņĢä ņČöĻ░ĆņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ░£ņāØļÉ£ ņåÉņŗżņØś ĻĘ£ļ¬©ļŖö ņ╗Ėļŗż. 2012ļģäĻ│╝ 2013ļģäņŚÉ ļ░£ņāØļÉ£ ņØ╝ņØ╝ ņåÉņŗżņĢĪņØĆ ņ▓Öļŗ╣ USD 5,000ņØ┤ ļäśņŚłļŗż. 2ļģä ļÅÖņĢłņŚÉļ¦ī ļ░£ņāØļÉ£ ņł£ņåÉņŗżņØś ĻĘ£ļ¬©ļŖö ņ▓Öļŗ╣USD 4Mļ│┤ļŗżĒü░ĻĘ£ļ¬©ņśĆļŗż. ņØ┤ņåÉņŗżĻĖłņĢĪņØĆņ┤łĻĖ░Ēł¼ņ×ģĻ│äņĢĮĻĖłņØä ņĀ£ņÖĖĒĢ£ ņåÉņŗż ņĢĪņłśļĪ£ ņŗżņĀ£ ņåÉņŗż ĻĘ£ļ¬©ļŖö ņØ┤ļ│┤ļŗż Ēø©ņö¼ Ēü¼ļŗż. ļ¦īņĢĮ AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņØ┤ ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņäĀļ░ĢņØś ņØĖļÅäļź╝ ĒżĻĖ░Ē¢łļŗżļ®┤, ļ¦ēļīĆĒĢ£ ņČöĻ░Ć ņåÉņŗżļÅä ņ×ģņ¦Ć ņĢŖņĢśņØä Ļ▓āņØ┤Ļ│Ā, 2012ļģäņŚÉ ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņäĀļ░ĢņØä ņ▓Öļŗ╣ USD 22MņŚÉ ĻĄ¼ņ×ģĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ņŚłļŗż. AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņØĆ 2011ļģäņŚÉ ļ▓ĢņĀĢĻ┤Ćļ”¼ļź╝ ņŗĀņ▓ŁĒ¢łļŗż.
ĻĄŁļé┤ ņŚģĻ│ä ņĀäļ¼ĖĻ░ĆļōżņØś ņäżļ¼Ė ņØæļŗĄņØä ļČäņäØĒĢ£ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļÅä ņĢ×ņä£ ņ¦äĒ¢ēļÉ£ ņé¼ļĪĆļČäņäØĻ│╝ Ļ░ÖņØ┤ Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖ ņØ┤ļĪĀņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ¬ģņŠīĒ׳ ņäżļ¬ģļÉ£ļŗż. ĻĖ░ļ░£ņŻ╝ļÉ£ ņäĀļ░ĢņØśņØĖļÅäņŚ¼ļČĆņŚÉļīĆĒĢ£ņäżļ¼ĖņØæļŗĄ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļÅä ļ¦żļ¬░ ļ╣äņÜ®ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņÖĆņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦ü ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļĪ£ ļ¦ēĒלņŚåņØ┤ ņäżļ¬ģļÉ£ļŗż.
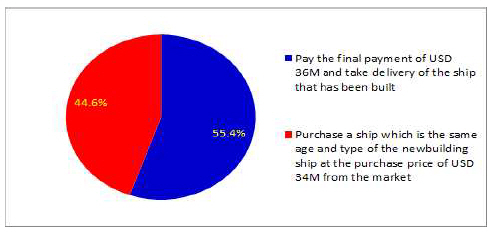
ņäżļ¼Ė1ļ▓łņŚÉņä£Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņżæņØĖņäĀļ░ĢņØśņØĖļÅäņ×öĻĖłĻ│╝ņŗ£ņןņŚÉņä£ļ¦żņ×ģĻ░ĆļŖźĒĢ£ ļÅÖņØ╝ ņäĀļĀ╣, ļÅÖĒśĢ ņäĀļ░ĢņØś Ļ░ĆĻ▓®ņØ┤ Ļ░ÖļŗżĻ│Ā Ļ░ĆņĀĢĒĢ£ Ļ▓ĮņÜ░, ņäżļ¼Ė ņØæļŗĄņ×É 56ļ¬ģņżæ 55ļ¬ģņØ┤ ĻĖ░ņĪ┤ņŚÉ ļ░£ņŻ╝ĒĢ£ ņäĀļ░ĢņØä ņØĖļÅäļ░øļŖöļŗżĻ│Ā ņØæļŗĄĒ¢łļŗż. Garland(1990)ļŖöļģ╝ļ¼ĖņŚÉņä£, ļ¦żļ¬░ļ╣äņÜ®ņØĆĒöäļĪ£ņĀØĒŖĖņØś ņ¦ĆņåŹņŚÉ ņ¦üņĀæņĀüņØĖ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ņżĆļŗżĻ│Ā ņŻ╝ņןĒ¢łļŗż. ņé¼ļĪĆ ļČäņäØņŚÉņä£ ņä£ņłĀņØæļŗĄņ×ÉļōżņØ┤ ņ¢ĖĻĖēĒĢ£ ĻĖ░ ļé®ļČĆļÉ£ Ļ│äņĢĮĻĖłĻ│╝ Ļ▒┤ņĪ░Ļ│äņĢĮ ņäĀĻ░Ć(USD 45M)Ļ░Ć ņäżļ¼ĖņØæļŗĄņØś ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņŚÉļÅä ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ│żļŗżĻ│Ā ĒīÉļŗ©ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż. ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņāü ļ¦żļ¬░ ļ╣äņÜ® ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņÖĆ ņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦ü ĒÜ©Ļ│╝Ļ░Ć ņŚåņŚłļŗżļ®┤ ĻĖ░ņĪ┤ ļ░£ņŻ╝ ņäĀļ░Ģ ņØĖļÅäņÖĆ ņŗ£ņןņŚÉņä£ ļÅÖņØ╝ ņäĀļĀ╣, ļÅÖĒśĢņäĀļ░Ģ ļ¦żņ×ģ Ļ░ä ļ╣äņ£©ņØ┤ ĒĢ£ņ¬Įņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ│╝ļÅäĒĢśĻ▓ī ņ╣śņÜ░ņ╣śņ¦ĆļŖö ņĢŖņĢśņØä Ļ▓āņØ┤ļŗż.
ļæÉļ▓łņ¦Ė ņäżļ¼Ė Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ ļ│┤ļ®┤, ņŗ£ņןņŚÉņä£ ļÅÖņØ╝ ņäĀļĀ╣, ļÅÖĒśĢ ņäĀļ░ĢņØś ļ¦żņ×ģ Ļ░ĆĻ▓®ņØ┤ Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ Ļ│äņĢĮĒĢ£ ņäĀļ░ĢņØś ņ×öĻĖł ņ¦ĆĻĖēņĢĪļ│┤ļŗż USD 2MņØ┤ ļé«ņĢśņØīņŚÉļÅä ļČłĻĄ¼ĒĢśĻ│Ā, 55.4%ņØś ņäżļ¼Ė ņ░ĖņŚ¼ņ×ÉĻ░Ć ĻĖ░ņĪ┤ņŚÉ ļ░£ņŻ╝ĒĢ£ ņäĀļ░ĢņØä ņØĖļÅä ļ░øĻ▓ĀļŗżĻ│Ā ņØæļŗĄĒ¢łļŗż. ņĀäĒåĄņĀü Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖņØś ĒÜ©ņÜ®ĻĘ╣ļīĆĒÖö ņØ┤ļĪĀņØä ņāØĻ░üĒĢ£ļŗżļ®┤, ļŗ╣ņŚ░Ē׳ ņäżļ¼Ė ņ░ĖņŚ¼ņ×É ņĀäņøÉņØ┤ USD 2MņØ┤ ņŗ╝ Re-sale ņäĀļ░ĢņØä ņŗ£ņןņŚÉņä£ ļ¦żņ×ģĒĢśļŖö ņäĀĒāØņØä Ē¢łņ¢┤ņĢ╝ Ē¢łļŗż.
ņĢ×ņä£ ņäżļ¬ģļÉ£ ņä£ņłĀ ņØæļŗĄņØś ļČäņäØ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØ┤, Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖ ņØ┤ļĪĀņØĖ ļ¦żļ¬░ļ╣äņÜ®ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņÖĆņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦ü ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļĪ£ ļæÉ ļ▓łņ¦Ė ņäżļ¼Ė ņØæļŗĄ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļŖö ļ¬ģņŠīĒ׳ ņäżļ¬ģļÉ£ļŗż. ĻĖ░ņĪ┤ņŚÉ ņØ┤ļ»Ė Ēł¼ņ×ģļÉ£ Ļ│äņĢĮĻĖłņØś ņśüĒ¢źĻ│╝, ņŗ£ņןļ¦żļ¦ż Ļ░ĆĻ▓® ļ│┤ļŗż ļåÆņØĆ Ļ▒┤ņĪ░Ļ│äņĢĮ ņäĀĻ░ĆņØś ņśüĒ¢źļź╝ ļ░øņĢä ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņäĀļ░ĢņØś Ļ░Ćņ╣śĻ░Ć ņĄ£ņåī USD 36M ļ│┤ļŗżļŖö ļåÆļŗżĻ│Ā ņāØĻ░üĒĢśņŚ¼ ņØæļŗĄņ×ÉļōżņØ┤ ņŗ£ņןĻ░ĆĻ▓®ļ│┤ļŗż ļåÆņØĆĻ▒┤ņĪ░ņäĀļ░ĢņØśņØĖļÅäļź╝ņäĀĒāØĒ¢łļŗżĻ│ĀļČäņäØļÉ£ļŗż. Putten et al.(2010)ņØĆ Ēł¼ņ×ÉĻ░Ć ņØ┤ļ»Ė ņ¦æĒ¢ēļÉ£ ĒöäļĪ£ņĀØĒŖĖņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░, ņé¼ļ×īļōżņØĆ ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ĒöäļĪ£ņĀØĒŖĖĻ░Ć ļ¦łļ¼┤ļ”¼ļÉśļÅäļĪØ Ļ│äņåŹ ņ¦äĒ¢ēĒĢśļĀżļŖö Ļ▓ĮĒ¢źņØ┤ ņ׳ļŗżĻ│Ā ņŻ╝ņןĒ¢łļŗż. Arkes and Blumer(1985)ļÅä ņäĀĒ¢ēļÉ£ Ēł¼ņ×ÉĻ░Ć ņ¦ĆņåŹņĀüņØĖ ņČöĻ░Ć Ēł¼ņ×É Ļ▓░ņŗ¼ņØä ņ£ĀļÅäĒĢ£ļŗżĻ│Ā ņŻ╝ņןĒ¢łļŗż. Ku et al.(2006)ļŖö ņ┤łĻĖ░Ļ░ÆņØ┤ ļ¦żļ¬░ļ╣äņÜ®ņØä ļ░£ņāØņŗ£Ēéżļ®┤ ņé¼ļ×īļōżņØĆ Ļ░Ćņ╣śĒÅēĻ░Ćļź╝ ņĀ£ļīĆļĪ£ ĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ¢┤ļĀĄļŗżĻ│Ā Ļ░ĢņĪ░Ē¢łļŗż.
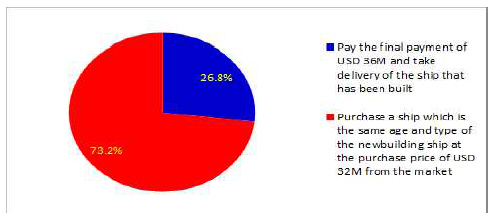
ņäĖļ▓łņ¦Ė ņäżļ¼ĖņØæļŗĄ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļÅä ļ¦żļ¬░ ļ╣äņÜ® ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņÖĆ ņŚźņ╣┤ ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļĪ£ ļ¦ēĒל ņŚåņØ┤ ņäżļ¬ģļÉ£ļŗż. 26.8%ņØś ņäżļ¼Ė ņ░ĖņŚ¼ņ×ÉļōżņØ┤ ĻĖ░ņĪ┤ņŚÉ ļ░£ņŻ╝ĒĢ£ ņäĀļ░ĢņØä ņØĖļÅäļ░øļŖöļŗżĻ│Ā ņØæļŗĄĒ¢łļŗż. ņŗ£ņןņŚÉņä£ ļ¦żņ×ģĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ļÅÖņØ╝ ņäĀļĀ╣, ļÅÖņØ╝ ņäĀĒśĢ ņäĀļ░ĢņØś Ļ░ĆĻ▓®ņØ┤ USD 4MņØ┤ļéś ļŹö ļé«ņĢśņØīņŚÉļÅä ļČłĻĄ¼ ĒĢśĻ│Ā, 26.8%ņØś ņäżļ¼Ė ņ░ĖņŚ¼ņ×ÉļōżņØĆ ĻĖ░ņĪ┤ņŚÉ ņ×ÉĻĖłņØ┤ Ēł¼ņ×ģļÉ£ ļ░£ņŻ╝ ņäĀļ░ĢņØä ņØĖļÅäļ░øļŖöļŗżĻ│Ā ļŗĄĒ¢łļŗż. ņĀäĒåĄņĀü Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖ ņØ┤ļĪĀņ£╝ļĪ£ļŖö ņäżļ¬ģĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ¢┤ļĀżņÜ┤ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØ┤ļØ╝Ļ│Ā ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż. Arkes and Ayton(1999)ņØĆ ĻĖ░ Ēł¼ņ×ģļÉ£ ņ×ÉņøÉņØ┤ ļéŁļ╣äņÖĆ ņåÉņŗżļĪ£ ĒÅēĻ░ĆļÉśĻĖ░ļź╝ ņøÉĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņŚÉ ņŗżĒī©Ļ░Ć ņśłņāüļÉśĻ▒░ļéś, ļ»ĖļלĻ░Ćņ╣śĻ░Ć ļé«ņØĆ ĒöäļĪ£ņĀØĒŖĖļź╝ Ļ│äņåŹ ņ¦äĒ¢ēĒĢ£ļŗżĻ│Ā ņŻ╝ņןĒ¢łļŗż. Tversky and Kahneman(1974)ņØĆ ņŗ£ņ×æņĀÉĻ│╝ ņĄ£ņ┤łĻ░ÆņØĆ ļ¦łņ¦Ćļ¦ē Ļ▓░ņĀĢņŚÉ ņ¦üņĀæņĀüņØĖ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣£ļŗżĻ│Ā Ļ░ĢņĪ░Ē¢łļŗż. Ļ▒┤ņĪ░Ļ│äņĢĮ Ļ░ĆĻ▓®ņØĖ USD 45MņØ┤ ņäżļ¼ĖņØæļŗĄņŚÉ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ│żļŗżĻ│Ā ļ│╝ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż.
ņāüĻĖ░ ņä£ņłĀ ņØæļŗĄ ļé┤ņÜ®Ļ│╝ ņäżļ¼Ė Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļČäņäØņØä ņĀäĒåĄņĀü Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖņŚÉņä£ ņŻ╝ņןĒĢśļŖö ĒÜ©ņÜ®ĻĘ╣ļīĆĒÖö ņØ┤ļĪĀ ļō▒ņ£╝ļĪ£ļŖö ļ¬ģņŠīĒ׳ ņäżļ¬ģĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ¢┤ļĀĄļŗż. ĻĘĖļ¤¼ļéś, ņØ┤ļ¤¼ĒĢ£ ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢļōżņØĆ Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖņŚÉņä£ ņĀĢņØśĒĢśļŖö ļ¦żļ¬░ ļ╣äņÜ® ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņÖĆ ņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦ü ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļĪ£ ļ¬ģĒÖĢĒ׳ ņäżļ¬ģļÉśļŖö Ļ▓āņØä ļ│Ė ļČäņäØņØä ĒåĄĒĢśņŚ¼ ĒÖĢņØĖ ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż.
ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£ĄĻĖ░Ļ┤ĆĻ│╝ ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ĻĖ░ņŚģļōżņØ┤ Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖņŚÉņä£ ņ¢ĖĻĖēĒĢ£ Ļ░üņóģ ņŚÉļ¤¼ļōżņØä ņØ┤ĒĢ┤ĒĢśĻ│Ā ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņŚÉ ņĀüņÜ®ĒĢ£ļŗżļ®┤, ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£ĄņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļ│┤ļŗż Ēśäļ¬ģĒĢśĻ│Ā, ĒĢ®ļ”¼ņĀüņØĖ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØä ņŗżĒ¢ēĒĢĀ Ļ▓āņØ┤ļ®░, ņØ┤ļŖö ļ¬©ļōĀ Ļ▒░ļל ļŗ╣ņé¼ņ×ÉņŚÉĻ▓ī ņØ┤ļĪ£ņÜ┤ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ ļÅäņČ£ĒĢĀ Ļ▓āņØ┤ļŗż.
Ē¢ēļÅÖĻ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖĻ│╝ Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņé¼ļ×īļōżņØś Ļ┤Ćņŗ¼ņØĆ ņŗ£Ļ░äņØ┤ ņ¦ĆļéĀņłśļĪØ ņŚ¼ļ¤¼ ļČäņĢ╝ņŚÉņä£ ļŖśņ¢┤ļéśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż. ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņé¼ļōżņØĆ ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£ĄņØä ņŗżĒ¢ēĒĢśļ®┤ņä£ ļĢīļĢīļĪ£ Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖņĀü ņśżļźśņØś ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ░øņĢä ļ╣äĒĢ®ļ”¼ņĀüņØĖ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØäņ¦äĒ¢ēĒĢśĻĖ░ļÅäĒĢśļ®░, ņØ┤ļĪ£ņØĖĒĢśņŚ¼ļ¦ēļīĆĒĢ£ņåÉņŗżņØä Ļ▓ĮĒŚśĒĢśĻĖ░ļÅä ĒĢ£ļŗż. ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą Ļ│╝ņĀĢņŚÉņä£ ļ░£ņāØļÉśļŖö ņØ┤ļ¤¼ĒĢ£ ļ╣äĒĢ®ļ”¼ņĀüņØĖ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢļōżņØĆ Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖ ņØ┤ļĪĀļōżļĪ£ ļ¼┤ļ”¼ņŚåņØ┤ ņäżļ¬ģļÉ£ļŗż.
AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņØś ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£ĄņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØĆ Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖ ņØ┤ļĪĀņŚÉ ļ¬ģņŗ£ļÉ£ ļ¦żļ¬░ ļ╣äņÜ® ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņÖĆ ņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦ü ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņØś ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ░øņØĆ ļ╣äĒĢ®ļ”¼ņĀüņØĖ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņ£╝ļĪ£ ļČäņäØ ļÉ£ļŗż.
2010ļģä AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ļŗ┤ļŗ╣ņ×ÉļŖö ņ║ĀņĮöņÖĆ ņŚģļ¼┤ĒśæņØśļź╝ ņ¦äĒ¢ē ĒĢśļ®┤ņä£ ņŚ¼ļ¤¼ ņ░©ļĪĆ Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņżæņØĖ Supramax ņäĀļ░ĢņØ┤ 2007ļģäĻ│╝ 2008ļģäņŚÉ USD 70M ņØ┤ņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ¦żļ¦żļÉśņŚłņŚłļŗżĻ│Ā Ļ░ĢņĪ░Ē¢łļŗż. ņØ┤ ļé┤ņÜ®ņØĆ ņä£ņłĀ ņØæļŗĄņä£ņŚÉļÅä ļ¬ģņŗ£ļÉśņ¢┤ņ׳ļŗż. ņØ┤ļ¤¼ĒĢ£ ļé┤ņÜ®ņØĆ Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖ ņØ┤ļĪĀ ņżæ ĒĢśļéśņØĖ ņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦ü ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņŚÉņä£ ņäżļ¬ģĒĢśļŖö ļé┤ņÜ®Ļ│╝ ņĀĢĒÖĢĒ׳ ņØ╝ņ╣śļÉ£ļŗż. Ļ▒░ĻĖ░ņŚÉ ļŹöĒĢśņŚ¼, AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņØś Ļ▓Įņśüņ¦äļōżņØĆ ĻĖ░ ļé®ļČĆļÉ£ ņŗĀņĪ░ Ļ│äņĢĮĻĖł 15% ņ”ē, ņé¼ņĀä Ēł¼ņ×ÉĻĖłņØś ņåÉņŗżņØä ņøÉĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņĢśļŗż. ņØ┤ ļśÉĒĢ£, Ē¢ēļÅÖ ņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖņØś ņØ┤ļĪĀ ņżæ ĒĢśļéśņØĖ ļ¦żļ¬░ ļ╣äņÜ® ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļĪ£ ļ¬ģņŠīĒ׳ ņäżļ¬ģļÉ£ļŗż.
AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņØ┤ ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ SupramaxņäĀļ░ĢņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņØĖļÅä ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£ĄņØä ņŗżĒ¢ēĒĢ£ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØĆ ĒĢ®ļ”¼ņĀüņØ┤ņŚłļŗżĻ│Ā ļ│┤ĻĖ░ņŚÉļŖö ļ¼┤ļ”¼Ļ░Ć ņ׳ļŗż. ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņ¦äĒ¢ēņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņŚģļ¼┤ ĒśæņØś ļŗ╣ņŗ£, ņ║ĀņĮöļŖö ņłśņ░©ļĪĆ ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņäĀļ░ĢņØś ņØĖļÅä ĒżĻĖ░ļź╝ ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņé¼ ļŗ┤ļŗ╣ņ×ÉļōżņŚÉĻ▓ī ĻČīņ£Ā Ē¢łņŚłļŗż. ļīĆĻĘ£ļ¬©ļĪ£ ļ░£ņŻ╝ļÉ£ ņäĀļ│Ąļ¤ē, ņĀäļ¼ĖĻ░ĆļōżņØś ļ▓īĒü¼ņäĀ ņŗ£ņןņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļČĆņĀĢņĀü Ļ▓¼ĒĢ┤, ĒĢśļØĮņäĖņØĖ ņŗ£ņןņäĀĻ░ĆņÖĆ ņÜ┤ņ×ä ļō▒ ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņäĀļ░ĢņØś Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ņĀü ļ»ĖļלĻ░Ćņ╣śĻ░Ć ļåÆņ¦Ć ņĢŖļŗżļŖö ĒĢ®ļ”¼ņĀü ņČöļĪĀņØ┤ Ļ░ĆļŖźĒ¢łĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņØ┤ņŚłļŗż. ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī, AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņØĆ ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ņäĀļ░ĢņØä ņØĖļÅäļ░øĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢśņŚ¼ ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņĪ░ļŗ¼ņØä ņŗżĒ¢ēĒ¢łļŗż. ĻĘĖļ¤¼ļéś, ņ║ĀņĮöņØś ņśłņāüļīĆļĪ£, ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņŗżĒ¢ē Ēøä AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņØĆ ņØĖļÅäļ░øņØĆ ņäĀļ░Ģļōż ļĢīļ¼ĖņŚÉ ļ¦ēļīĆĒĢ£ ņČöĻ░Ć ņåÉņŗżņØä ņ×ģņŚłļŗż.
ņä£ņłĀņØæļŗĄņØä ļČäņäØĒĢ£ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝, ļ¦żļ¬░ ļ╣äņÜ® ņśżļźśņÖĆ ņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦ü ĒÜ©Ļ│╝Ļ░Ć AĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņØś ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņŚÉ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ņŻ╝ņŚłļŗżļŖö ņé¼ņŗżņØä ņØĖņ¦ĆĒĢśĻ▓ī ļÉśņŚłļŗż. ņØ┤ļ¤¼ĒĢ£ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢļōżņØĆ Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖ ņØ┤ļĪĀļōżļĪ£ ļ¬ģĒÖĢĒ׳ ņäżļ¬ģļÉśļ®░, ļ¬ģņŗ£ļÉ£ Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖņĀü ņśżļźśņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ£ ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØ┤ ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņé¼ņŚÉ ļ¦ēļīĆĒĢ£ ņåÉņŗżņØä ņ£Āļ░£ņŗ£ņ╝░ļŗżļŖö ļČäņäØ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļÅä ņĢīĻ▓ī ļÉśņŚłļŗż. ņāüĻĖ░ ļČäņäØņØä ņóģĒĢ®ĒĢ┤ ļ│Ė Ļ▓░Ļ│╝, Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖņĀü ņśżļźśļōżņØĆ ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņé¼Ļ░Ć ņäĀļ░Ģ ĻĖłņ£ĄņØä ņ¦äĒ¢ēĒĢśļŖö Ļ│╝ņĀĢņŚÉ ņ¦üņĀæņĀüņØĖ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ņżä ņłś ņ׳Ļ│Ā, ņØ┤ļĪ£ ņØĖĒĢ┤ ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņé¼ļŖö ļ╣äĒĢ®ļ”¼ņĀüņØĖ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØä ļé┤ļ”┤ ņłś ņ׳ļŗżļŖö ņé¼ņŗżņØä ņĢīĻ▓ī ļÉśņŚłļŗż.
ņäżļ¼ĖņØæļŗĄ 1ļ▓ł, 2ļ▓ł, 3ļ▓łņØś ļČäņäØ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ņŚÉ ļö░ļź┤ļ®┤, ņä£ņłĀ ņØæļŗĄ ļČäņäØ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ņÖĆļ¦łņ░¼Ļ░Ćņ¦ĆļĪ£ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢļé┤ņÜ®ļōżņØä ļ¬ģĒÖĢĒĢśĻ▓ī ļ¦żļ¬░ ļ╣äņÜ® ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņÖĆ ņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦ü ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļĪ£ ņäżļ¬ģĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż. ņĀäĒåĄņĀü Ļ▓ĮņĀ£ĒĢÖņŚÉņä£ ņŻ╝ņןĒĢśļŖö ĒÜ©ņ£© ĻĘ╣ļīĆĒÖö ņØ┤ļĪĀņØä ļö░ļźĖļŗżļ®┤, ļ¬©ļōĀ ņäżļ¼Ė ņ░ĖņŚ¼ņ×ÉļŖö ĻĖ░ņĪ┤ņŚÉ ļ░£ņŻ╝ĒĢ£ ņäĀļ░ĢņØś ņØĖļÅäļź╝ ĒżĻĖ░ĒĢśĻ│Ā, ņŗ£ņןņŚÉņä£ ņØĖļÅä ņśłņĀĢ ņäĀļ░Ģļ│┤ļŗż Ļ░ĆĻ▓®ņØ┤ ļé«ņØĆ ļÅÖņØ╝ ņäĀļĀ╣, ļÅÖĒśĢ ņäĀļ░Ģ ļ¦żņ×ģņØä ņäĀĒāØĒ¢łņ¢┤ņĢ╝ Ē¢łļŗż. ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī, USD 2MņØ┤ ļ╣äņīīņØīņŚÉļÅä ļČłĻĄ¼ĒĢśĻ│Ā 55.4%ņØś ņäżļ¼Ė ņØæļŗĄņ×ÉļōżņØ┤ ĻĖ░ņĪ┤ņŚÉ ļ░£ņŻ╝ ĒĢśņŚ¼ Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ņżæņØĖ ņäĀļ░ĢņØä ņØĖļÅäļ░øļŖöļŗżĻ│Ā ņØæļŗĄĒ¢łļŗż. Ļ▒░ĻĖ░ņŚÉ ļŹöĒĢśņŚ¼, USD 4MņØ┤ ļ╣äņŗ╝ Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ņŚÉļÅä 26.8%ņØś ņØæļŗĄņ×ÉļōżņØ┤ ĻĖ░ņĪ┤ ļ░£ņŻ╝ ņäĀļ░ĢņØä ņØĖļÅäļ░øļŖöļŗżĻ│Ā ļŗĄĒ¢łļŗż.
ņäżļ¼Ė 1ļ▓ł, 2ļ▓ł, 3ļ▓ł ņ░ĖņŚ¼ņ×Éļōż ņżæ ņäĀļ░Ģ ņØĖļÅä ņ×öĻĖłņØä ļé®ļČĆĒĢśĻ│Ā, ĻĖ░ņĪ┤ ļ░£ņŻ╝ ņäĀļ░ĢņØä ņØĖļÅä ļ░øļŖöļŗżļŖö ņØæļŗĄņØä ĒĢ£ ņäżļ¼Ė ņØæļŗĄņ×ÉļōżņØĆ ņäĀļ░Ģ ļ░£ņŻ╝ Ļ░ĆĻ▓®ņŚÉņä£ ņŚźņ╣┤ļ¦ü ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ░øņĢśĻ│Ā, ĻĖ░ņĪ┤ņŚÉ ļé®ļČĆļÉ£ Ļ│äņĢĮĻĖłņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØĖĒĢ£ ļ¦żļ¬░ ļ╣äņÜ® ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņØś ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ░øņĢä ĻĘĖļ¤¼ĒĢ£ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØä ņ¦äĒ¢ēĒ¢łļŗżĻ│Ā ļČäņäØļÉ£ļŗż. ņØ┤ļ¤¼ĒĢ£ņäżļ¼ĖņØæļŗĄņ×ÉļōżņØśņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØĆĒ¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖ ņØ┤ļĪĀļōżļĪ£ ļ¬ģņŠīĒĢśĻ▓ī ņäżļ¬ģļÉśĻ│Ā ļČäņäØļÉ£ļŗż.
ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ĒÜīņé¼ņØś Ļ▓Įņśüņ¦äļōżņØĆ ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£ĄņØä ņ¦äĒ¢ēĒĢśļ®┤ņä£, ļ╣äĒĢ®ļ”¼ņĀüņØĖ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØä ļé┤ļ”┤ Ļ▓ĮņÜ░Ļ░Ć ļ╣łļ▓łĒĢśĻ▓ī ļ░£ņāØĒĢĀ Ļ▓āņØ┤ļŗż. ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØä ņ¦äĒ¢ēĒĢĀ ļĢī ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą ļŗ┤ļŗ╣ņ×ÉļōżņØĆ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØä ĒĢśļŖö Ļ│╝ņĀĢņŚÉņä£ Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖņŚÉņä£ ņ¢ĖĻĖēļÉśļŖö ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢ ņŚÉļ¤¼ļōżņØ┤ ņĪ┤ņ×¼ ĒĢśļŖöņ¦Ć Ļ▓ĆĒåĀĒĢĀ ĒĢäņÜöĻ░Ć ņ׳ļŗż.
ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£ĄņŚÉ Ļ┤ĆĒĢ£ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØä ņ¦äĒ¢ēĒĢśļ®┤ņä£, ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņé¼ļōżņØ┤ ņ¢┤ļ¢ĀĒĢ£ ņØ┤ņ£ĀļĪ£ ļ╣äĒĢ®ļ”¼ņĀüņØĖ ņØśņé¼Ļ▓░ņĀĢņØä ņ¦äĒ¢ēĒĢśĻ▓ī ļÉśļŖöņ¦ĆņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļ░░Ļ▓ĮĻ│╝ ņØ┤ņ£ĀļōżņØĆ Ē¢ēļÅÖņ×¼ļ¼┤ĒĢÖ ņØ┤ļĪĀļōżņØä ĒåĄĒĢ┤ņä£ ņäżļ¬ģļÉĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż.
REFERENCES
1. Ang, I.2007), ŌĆśKorean spends $264m on bulkŌĆÖ, TradeWinds, August 23, 2007, https://www.tradewindsnews.com/weekly/korean-spends-264m-on-bulk/1-1-110281..
2. Ariely, D. and Simonson, I.(2003 ŌĆśBuying, bidding, playing, or competing? Value assessment and decision dynamics in online auctionsŌĆÖ, Journal of Consumer Psychology, 13 (1&2), pp. 113-123.
3. Arkes, H. R.(1996 ŌĆśThe psychology of wasteŌĆÖ, Journal of Behavioural Decision Making, 9, pp. 213-224.
4. Arkes, H. R. and Blumer, C.(1985 ŌĆśThe psychology of sunk costŌĆÖ, Organizational Behaviour and Human Decision Processes, 35, pp. 124-140.
5. Arkes, H. R. and Ayton, P.(1999 ŌĆśThe sunk cost and concorde effects: Are humans less rational than lower animals?ŌĆÖ, Psychological Bulletin, 125(5), pp. 591-600.
6. Baddeley, M.(2017), Behavioural Economics: A Very Short Introduction, 1st edn. Oxford University Press.
7. Barberis, N. and Thaler, R.2002), A survey of behavioural finance, National Bureau of Economic Research.
8. Bell, E.,, Bryman, A. and Harley, B.(2019), Business research methods, 5thedn. NewYork: Oxford University Press..
9. Bu, D. J.2009), ŌĆśņ║ĀņĮö ņ▓½ ņäĀļ░ĢĒÄĆļō£ ņøÉĻ░ĆļČäņäØĒ¢łļŹöļŗł..ŌĆÖ, Shipping Daily, July 17, 2009, http://www.shippingdaily.co.kr/news_view.php?num=60620.
10. Camerer, C. F.,, Loewenstein, G. and Rabin, M.(2004), ŌĆśAdvances in behavioral economicsŌĆÖ, New Jersey: Princeton University Press.
11. Chang, T. P. and Chou, R. Y.(2018 ŌĆśAnchoring effect on macroeconomic forecasts: A heterogeneity approachŌĆÖ, Romanian Journal of Economic Forecasting, XXI(4)..
12. Chen, C. S.,, Cheng, J. C.,, Lin, F. C. and Peng, C.(2017 ŌĆśThe role of house money effect and availability heuristic in investor behaviourŌĆÖ, Management Decision, 55(8), pp. 1598-1612.
13. Cho, I.,, Wesslen, R.,, Karduni, A.,, Santhanam, S.,, Shaikh, S. and Dou, S.2017), ŌĆśThe anchoring effect in decision-making with visual analyticsŌĆÖ, IEEE Conference onVisual Analytics Science and Technology, October 1-6.
14. Clarksons.net2019), ŌĆśShipping Intelligence NetworkŌĆÖ, https://sin.clarksons.net/.
15. Clarkson Research Services(2007), ŌĆśShipping Intelligence WeeklyŌĆÖ, Clarkson Research Services Limited, Issue No. 785, August 31, 2007.
16. Creswell, J. W.(2013 Qualitative inquiry and research design: Choosing among five traditions. ņĪ░ĒØźņŗØ ņÖĖ ņŚŁ (2015). <ņ¦łņĀü ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļ░®ļ▓ĢļĪĀ: ļŗżņä» Ļ░Ćņ¦Ć ņĀæĻĘ╝>. ņä£ņÜĖ: ĒĢÖņ¦Ćņé¼..
17. DART2019), DART database website, http://dart.fss.or.kr.
18. Dick A. S. and Lord, K. R.(1998 ŌĆśThe impact of membership fees on consumer attitude and choiceŌĆÖ, Psychology & Marketing, 15(1), pp. 41-58.
19. Drewry maritime research2011), Ship Operating Costs- 2011/2012.
20. Englich, B. and Mussweiler, T.(2001 ŌĆśSentencing Under Uncertainty: Anchoring Effects in the CourtroomŌĆÖ, Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 31, 7, pp. 1535-1551.
21. Englich, B.,, Mussweiler, T. and Strack, F.(2005 ŌĆśThe Last Word in Court - A Hidden Disadvantage for the DefenseŌĆÖ, Law and Human Behavior, Vol. 29, No. 6, pp. 705-722.
22. Fiske, S. T. and Taylor, S. E.(1991), Social Cognition. New York: McGraw-Hill..
23. Forbes, W.(2009), Behavioural finance, West Sussex: John Wiley & Sons Ltd..
24. Friedman, D.,, Pommerenke, K.,, Lukose, R.,, Milam, G. and Huberman, B. A.(2007 ŌĆśSearching for the sunk cost fallacyŌĆÖ, Exp Econ (2007), 10, pp. 79-104.
25. Garland, H.(1990 ŌĆśThrowing good money after bad: The effect of sunk costs on the decision to escalate commitment to an ongoing projectŌĆÖ, Journal of Applied Psychology, 75(6), pp. 728-731.
26. Garland, H. and Newport, S.(1991 ŌĆśEffects of absolute and relative sunk costs on the decision to persist with a course of actionŌĆÖ, Organizational Behaviour and Human Decision Processes, 48, pp. 55-69.
27. Gourville, J. T. and Soman, D.(1998 ŌĆśPayment depreciation: The behavioural effects of temporally separating payments from consumptionŌĆÖ, Journal of Consumer Research, 25(2), pp. 160-174.
28. Haita-Falah, C.(2017 ŌĆśSunk-cost fallacy and cognitive ability in individual decision-makingŌĆÖ, Journal of Economic Psychology, 58, pp. 44-59.
29. Harwood, S.(1995), Shipping finance, 2ndedn. ,EuromoneyInstitutionalInvestor..
30. Ho, T. H.,, Png, I. P. L. and Reza, S.(2018 ŌĆśSunk cost fallacy in driving the worldŌĆÖs costliest carsŌĆÖ, Management Science, 64(4), pp. 1761-1778.
31. Jeon, H. J.,, Yun, H. S. and Choi, Y. J.2017), ŌĆ£ņÜ░ļ”¼ļéśļØ╝ ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ĻĖłņ£ĄņØś ĒĢ£Ļ│ä ļ░Å ļ░£ņĀäļ░®Ē¢źŌĆØ, ĒĢ£ĻĄŁĒĢ┤ņ¢æņłśņé░Ļ░£ļ░£ņøÉ, Ēśä ņĢłņŚ░ĻĄ¼ 2017-01..
32. Infomax2020), Infomax Database Terminal, Korea Asset Management Corporation..
33. Kahneman, D.(2011), Thinking fast and slow, New York: Farror, Straus and Giroux..
34. Keasey, K. and Moon, P.(2000 ŌĆśSunk cost effect: a test of the importance of contextŌĆÖ, Economic Letters, 66(2), pp. 55-58.
35. Keefer, Q. A. W.(2015 ŌĆśPerformance feedback does not eliminate the sunk-cost fallacy: Evidence from professional footballŌĆÖ, J Labor Res, 36, pp. 409-426.
36. Keefer, Q. A. W.(2018 ŌĆśDecision-making beliefs and the sunk-cost fallacy: Major Leagure BaseballŌĆÖs final-off salary arbitration and utilizationŌĆÖ, Journal of Economic Psychology.
37. Kim, H. S. and Park, Y. Y.2016), ŌĆ£ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ņé¼ ļČĆņŗżļÅäļ»ĖļģĖŌĆ” ņØĆĒ¢ē ņŗżņĀüĻ│ĄĒż ĒśäņŗżļĪ£ŌĆØ, ļ¦żņØ╝Ļ▓ĮņĀ£, https://www.mk.co.kr/news/economy/view/2016/04/306025/.
38. Klonoski, R.(2013 ŌĆśThe case for case studies: Deriving theory from evidenceŌĆÖ, Journal of Business Case Studies, 9(3).
39. Ku, G.,, Galinsky, A. D. and Murnighan, J. K.(2006 ŌĆśStarting low but ending high: A reversal of the anchoring effect in auctionsŌĆÖ, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 90(6), pp. 975-986.
40. Kwak, Y. S.2010), ŌĆśļīĆĒĢ£ĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ 58K ņŗĀņĪ░ ļ▓īņ╗ż ņØĖņłśŌĆÖ, Maritime Press, Aug 06, 2010 http://www.maritimepress.co.kr/news/articleView.html?idxno=78059..
41. Liao, L. C.,, Chou, R. Y. and Chiu, B.(2013 ŌĆśAnchoring effect on foreign institutional investorsŌĆÖ momentum trading behaior: Evidence from the Taiwan stock marketŌĆÖ, North American Journal of Economics and Finance, 26, pp. 72-91.
42. Ludwig, T. and Tholen, J.2006), ŌĆśShipbuilding in China and its impacts on European shipbuilding industryŌĆÖ, Institute Labour and Economy, University of Bremen. http://www.iaw.uni-bremen.de/ccm/navigation/index.en .
43. Mussweiler, R. and Strack, F.(2000 ŌĆśThe use of category and exemplar knowledge in the solution of anchoring tasksŌĆÖ, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 78(6), pp. 1038-1052.
44. Mussweiler, T.,, Strack, F. and Pfeiffer, T.(2000 ŌĆśOvercoming the inevitable anchoring effect: Considering the opposite compensates for selective accessibilityŌĆÖ, Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 26(9), pp. 1142-1150.
45. Northcraft, G. B. and Neale, M. A.(1987 ŌĆśExperts, amateurs and real estate: An anchoring-andadjustment perspective on property pricing decisionsŌĆÖ, Organisational Behaviour and Human Decision Processes, 39, pp. 84-97.
46. Putten, M. V.,, Zeelenberg, M. and Dijk, E. V.(2010 ŌĆśWho throws good money after bad? Action vs. state orientation moderates the sunk cost fallacyŌĆÖ, Judgment and Decision Making, 5(1), pp. 33-36..
47. Rego, S.,, Arantes, J. and Magalhaes, P.(2018 ŌĆśIs there a sunk cost effect in committed relationships?ŌĆÖ, Current Psychology, 37, pp. 508-519.
48. Ritter, J. R.(2003 ŌĆśBehavioral financeŌĆÖ, Pacific-Basin Finance Journal, 11, pp. 429-437.
49. Sand, P.2010), ŌĆśDRY BULK SHIPPING - CAPESIZE FLOOD IS UNDERMINING FREIGHT RATESŌĆÖ, BIMCO, August 12, 2010, https://www.bimco.org/news/market_analysis/2010/0812_dry_bulk_shipping..
50. Seok, Y. S.2020), ŌĆ£[ĻĖ┤ĻĖēņĀÉĻ▓Ć-ķ¤ōņĪ░ņäĀĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ ĒÖ£ļĪ£ļŖö ņäĀļ░ĢĻĖłņ£Ą] ŌæĪ ļ»╝Ļ░äĻĖłņ£Ąņé¼, ĒĢ£ņ¦äĒĢ┤ņÜ┤ ņé¼Ēā£ ņØ┤Ēøä ŌĆśĒł¼ņ×É ĻĖ░Ēö╝ņ”ØŌĆÖ ŌĆÖŌĆÖ, ņĢäņŻ╝Ļ▓Į ņĀ£, https://www.ajunews.com/view/20200310133149075..
51. Shiller, R. J.,, Konya, F. and Tsutsui, Y.(1996 ŌĆśWhy did the Nikkei crash? expanding the scope of expectations data collectionŌĆÖ, The Review of Economics and Statistics, 78(1), pp. 156-164.
52. Shiller, R. J.(1998 Human behavior and the efficiency of the financial system, National Bureau of Economic Research.
53. Shipping Daily2011), ŌĆśļÅäĒæ£ļē┤ņŖż/ņ║ĀņĮö ņäĀļ░Ģ ņāüņäĖ ļé┤ņŚŁŌĆÖ, Shipping Daily, April 25, 2011, http://www.shippingdaily.co.kr/news_view.php?num=78399.
54. Stake R.(1995), The art of case study research, Sage, Los Angeles, California..
55. Stopford, M.(2009), Maritime economics, 3rd edn., Oxon: Routledge.
56. Stopford, M.2009), ŌĆśGlobalization & the Long Shipping CycleŌĆÖ, Clarkson Research, Royal Institute of Naval Architects..
57. Tan, H. T. and Yates, J. F.(1995 ŌĆśSunk cost effects: The influences of instruction and future return estimatesŌĆÖ, Organizational Behaviour and Human Decision Processes, 63(3), pp. 311-319.
58. Tversky, A. and Kahneman, D.(1974 ŌĆśJudgement under uncertainty: Heuristics and biasesŌĆÖ, Science, Vol. 185(4), pp. 1124-1131.
59. Tversky, A. and Kahneman, D.(1981 ŌĆśThe framing of decisions and the psychology of choiceŌĆÖ, Science, Vol. 211(4), pp. 453-458.
60. Verousis, T. and Gwilym, O. A.(2014 ŌĆśThe implications of a price anchoring effect at the upstairs market of the London Stock ExchangeŌĆÖ, International Review of Financial Analysis, 32, pp. 37-46.
61. Whyte, G. and Sebenius, J. K.(1997 ŌĆśThe effect of multiple anchors on anchoring in individual and group judgmentŌĆÖ, Organizational Behaviour and Human Decision Processes, 69(1), pp. 75-85.
62. Wilkinson, N. and Klaes, M.(2012), An introduction to behavioral economics, London: Palgrave Macmillan.
63. Wright, W. F. and Anderson, U.(1989 ŌĆśEffects of situation familiarity and financial incentives on use of the anchoring and adjustment heuristic for probability assessmentŌĆÖ, Organizational Behaviour and Human Decision Processes, 44, pp. 68-82.
64. Yin, R. K.(2009), Case study research: Design and methods (4th Ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage. .
65. Yin, R. K.(2014), Case study research: Designs and methods, Sage, Los Angeles, California. .
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 0 Crossref
- 0 Scopus
- 3,603 View
- 54 Download
- Related articles
-
The Effect of Towline and Bridle on the Slewing Motion of Barge2011 August;35(6)
The Effect of Warehouse Layout Design on Order Picking Efficiency2009 September;33(7)




 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print